
- Bioactive Compounds
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleckchem.com to customize your library.
You could select:
- Antibodies
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-Flag magnetic beads
- Anti-Flag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Magnetic Separator
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- New Products
- Contact Us
Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1)
Thiamine or vitamin B1 is a water-soluble vitamin of the B complex, its phosphate derivatives are involved in many cellular processes.
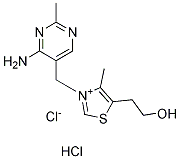
Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) Chemical Structure
CAS No. 67-03-8
Purity & Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.99%
99.99
Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) Related Products
| Related Products | Trolox Nicotinic Acid Sodium ascorbate Amprolium HCl Thiamine pyrophosphate hydrochloride Ergosterol Fursultiamine D-Pantothenate Sodium | Click to Expand |
|---|---|---|
| Related Compound Libraries | Metabolism Compound Library Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound Library Lipid Metabolism Compound Library | Click to Expand |
Biological Activity
| Description | Thiamine or vitamin B1 is a water-soluble vitamin of the B complex, its phosphate derivatives are involved in many cellular processes. |
|---|
| In vitro | ||||
| In vitro | Thiamine (50 mM), in addition to its nutritional value, induces systemic acquired resistance (SAR) in rice, tobacco, cucumber, and Arabidopsis. Thiamine-treated rice, Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), and vegetable crop plants shows resistance to fungal, bacterial, and viral infections. Thiamine treatment induces the transient expression of pathogenesis-related (PR) genes in rice and other plants. In addition, Thiamine treatment potentiates stronger and more rapid PR gene expression and the up-regulation of protein kinase C activity. [1] Vitamin B1 (10 μM) prevents acetaldehyde-induced inhibition of myocyte shortening in adult rat ventricular myocytes. Vitamin B1 (10 μM) effectively blunts the acetaldehyde-induced depression in ±dL/dt in adult rat ventricular myocytes. Vitamin B1 (10 μM) prevents acetaldehyde-induced shortening of time-to-peak shortening in adult rat ventricular myocytes. Vitamin B1 (10 μM) prevents acetaldehyde-induced elevation in both protein carbonyl formation and caspase-3 activation in adult rat ventricular myocytes. [2] Thiamine uptake is energy- and temperature-dependent, pH-sensitive, Na+-independent, saturable at both the nanomolar (apparent Km, 30 nM) and the micromolar (apparent Km, 1.72 mM) concentration ranges in ARPE-19 cells. Uptake of Thiamine is adaptively regulated by extracellular substrate level via transcriptionally mediated mechanisms that involve both hTHTR-1 and hTHTR-2 in ARPE-19 cells, it is also regulated by an intracellular Ca2+-calmodulin-mediated pathway. [3] Thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anemia (TRMA) fibroblasts are rescued from death with 10 nM-30 nM Thiamine (in the range of normal plasma thiamine concentrations). Normal fibroblasts exhibits saturable, high-affinity thiamine uptake (Km 400 nM-550 nM; Vmax 11 pmol/min/1×106 cells), while TRMA fibroblasts lacks detectable high-affinity uptake. At 30 nM Thiamine, the rate of uptake of Thiamine by TRMA fibroblasts is 10-fold less than that of wild-type, which explains the increased apoptosis of TRMA fibroblasts. [4] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
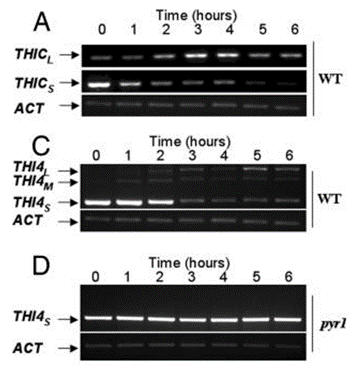
| Experimental Result Images | Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
| Western blot | THICL / THICS / THI4L / THI4M / THI4S / ACT Bax / Bid / p53 / p84 Rpb1 / Fcp1 / f-Rpb3 / Tfg3 / Rpb7 / Rpb4 |
|
18093957 | |
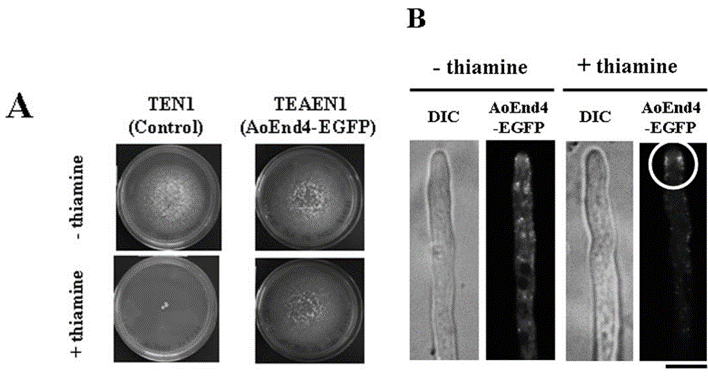
| Growth inhibition assay | TEN1 and TEAEN1 strains hippocampal Dcx+ cells |
|
19028995 | |
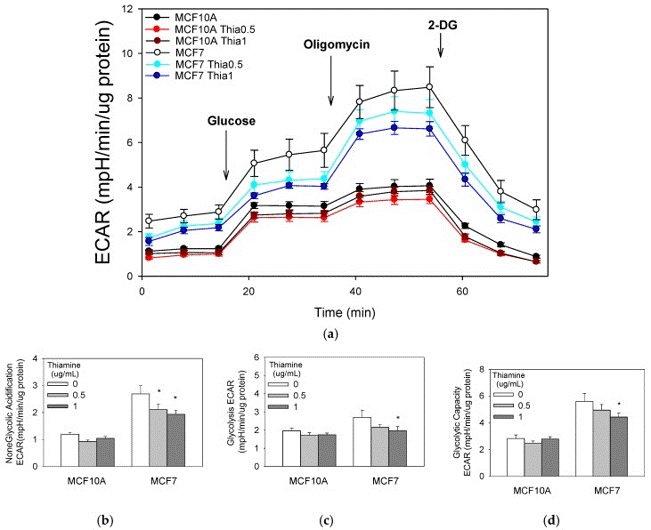
| Glycolysis stress test | Glycolysis stress |
|
29914147 | |
| Cell death | Cell survival |
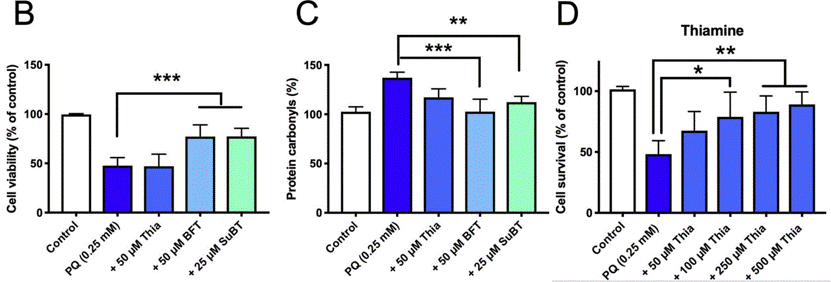
|
31193162 | |
| Western blot / RNA Blot | PR-1 / rRNA PR-1 / rRNA |
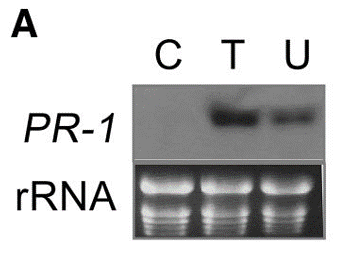
|
15980201 | |
| Immunofluorescence | Thi76KR / Thi7M399R / ThiN350K |
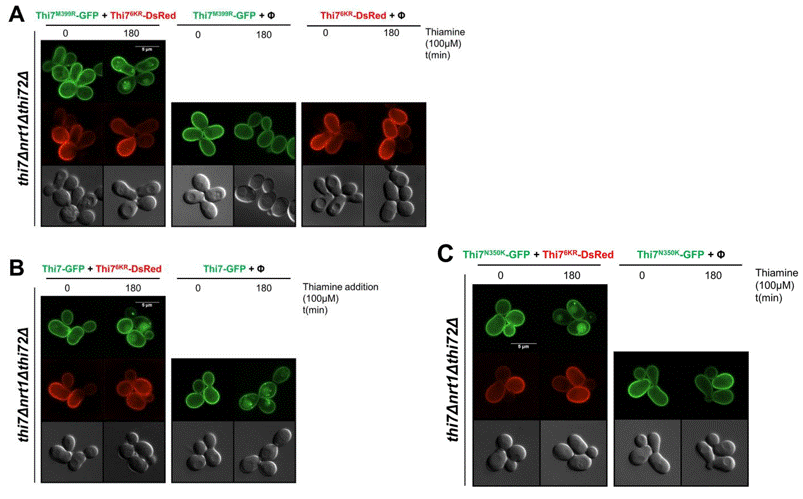
|
31658248 | |
| In Vivo | ||
| In vivo | Thiamine deficiency results in amyloid precursor protein immunoreactivity accumulated in swollen neurites within, or around lesions in rats, or in abnormal clusters in mice. [5] | |
|---|---|---|
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT06298344 | Recruiting | Congenital Heart Disease|Thiamine Deficiency|Patent Ductus Arteriosus|Ventricular Septal Defect|Atrial Septal Defect |
Universitas Sumatera Utara |
May 1 2024 | Early Phase 1 |
| NCT06326996 | Not yet recruiting | Coronary Heart Disease|Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting |
University of California Los Angeles |
May 2024 | Not Applicable |
| NCT06322212 | Not yet recruiting | Type2diabetes |
University of California Los Angeles |
April 2024 | Not Applicable |
| NCT06323538 | Not yet recruiting | Dietary Exposure|Diabetes Mellitus Type 2|Cardiovascular Diseases|Bone Loss|Sustainability|Exposure|Obesity|Vitamin Deficiency|Mineral Deficiency |
German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment|Max Rubner-Institut|University of Bonn|Research Institute for Plant-Based Nutrition|University of Jena|University of Regensburg|Heidelberg University|University of Vienna |
April 1 2024 | -- |
Chemical Information & Solubility
| Molecular Weight | 337.27 | Formula | C12 H17N4OS.HCl |
| CAS No. | 67-03-8 | SDF | Download Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) SDF |
| Smiles | CC1=C(SC=[N+]1CC2=CN=C(N=C2N)C)CCO.Cl.[Cl-] | ||
| Storage (From the date of receipt) | |||
|
In vitro |
Water : 67 mg/mL DMSO : Insoluble ( Moisture-absorbing DMSO reduces solubility. Please use fresh DMSO.) Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molecular Weight Calculator |
|
In vivo Add solvents to the product individually and in order. |
In vivo Formulation Calculator |
||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Molarity Calculator
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Tech Support
Answers to questions you may have can be found in the inhibitor handling instructions. Topics include how to prepare stock solutions, how to store inhibitors, and issues that need special attention for cell-based assays and animal experiments.
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
* Indicates a Required Field
Tags: buy Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) ic50 | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) price | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) cost | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) solubility dmso | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) purchase | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) manufacturer | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) research buy | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) order | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) mouse | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) chemical structure | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) mw | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) molecular weight | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) datasheet | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) supplier | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) in vitro | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) cell line | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) concentration | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) nmr






































