
- Inhibitors
- By product type
- Natural Products
- Inducing Agents
- Peptides
- Antibiotics
- Antibody-drug Conjugates(ADC)
- PROTAC
- Hydrotropic Agents
- Dyes
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
By research - Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-II
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleckchem.com to customize your library.
You could select:
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-DYKDDDDK Tag magnetic beads
- Anti-DYKDDDDK Tag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- Featured Products
- MRTX1133
- Nab-Paclitaxel
- KP-457
- IAG933
- RMC-6236 (Daraxonrasib)
- RMC-7977
- Zoldonrasib (RMC-9805)
- GsMTx4
- Navitoclax (ABT-263)
- TSA (Trichostatin A)
- Y-27632 Dihydrochloride
- SB431542
- SB202190
- MK-2206 Dihydrochloride
- LY294002
- Alisertib (MLN8237)
- XAV-939
- CHIR-99021 (Laduviglusib)
- Bafilomycin A1 (Baf-A1)
- Thiazovivin (TZV)
- CP-673451
- Verteporfin
- DAPT
- Galunisertib (LY2157299)
- MG132
- SBE-β-CD
- Tween 80
- Bavdegalutamide (ARV-110)
- Z-VAD-FMK
- Wnt-C59 (C59)
- IWR-1-endo
- (+)-JQ1
- 3-Deazaneplanocin A (DZNep) Hydrochloride
- RepSox (E-616452)
- Erastin
- Q-VD-Oph
- Puromycin Dihydrochloride
- Cycloheximide
- Telaglenastat (CB-839)
- A-83-01
- Ceralasertib (AZD6738)
- Liproxstatin-1
- Emricasan (IDN-6556)
- PMA (Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate)
- Dibutyryl cAMP (Bucladesine) sodium
- Nedisertib (M3814)
- PLX5622
- IKE (Imidazole Ketone Erastin)
- STM2457
- Saruparib (AZD5305)
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP use a biological nanosurface technology (S-TEC). Protein A/G is orientated as a coat on the surface of super paramagnetic microspheres with high coating density up to 9.3 × 1013 molecules/cm2.
Selleck's Has Been Cited by 363 Publications
Advantages
Spinning free, IP (takes <30 minutes) with minimal sample loss.
Background caused by non-specific binding is very low.
Beads contain 9.3×1013 molecules/cm2 of protein A/G. Antibody binding capacity up to 0.4-0.5 mg/mL.
Cheap to 73 USD/mL
Price Comparison
Description
Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP use a biological nanosurface technology (S-TEC). Protein A/G is orientated as a coat on the surface of super paramagnetic microspheres with high coating density up to 9.3 × 1013 molecules/cm2. Compared to other similar immune magnetic beads, Selleck MagBeads™ Protein A/G display more antibody binding sites, therefore during IP, less magnetic beads are used. Non-specific binding is low, enabling Selleck MagBeads Protein A/G to be used in IP conveniently and efficiently. With a large, specific surface area, these beads can greatly shorten the equilibrium antibody and antigen adsorption time, enabling complete antibody antigen adsorption process within 10 minutes, and complete total purification and precipitation in just 30 minutes. This product can be used on a wide variety of samples, such as in cell lysates, supernatants collected from cell secretion, serum, ascites, and other immune antigens.
Specificity
Protein A/G magnetic beads are affinity purification magnetic beads prepared by separately coupling recombinant Protein A and recombinant Protein G to the surface of magnetic beads. Protein A contains four IgG Fc binding regions, while Protein G possesses two IgG Fc binding regions. Protein A/G magnetic beads combine the advantages of both Protein A and Protein G, enabling efficient capture and purification of a wide range of IgG antibodies from various species and subclasses. Compared to using Protein A or Protein G individually, Protein A/G magnetic beads exhibit stronger IgG binding capacity and are less affected by pH fluctuations during the binding process.
Properties
| Concentration | 10 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Particle size | 100 nm |
| Binding capacity of human IgG | 0.4-0.5 mg/mL |
| Ligand | Recombinant protein A/G |
| Application | Protein Purification, Immunoprecipitation |
| pH stability | 6-8 (Long term) |
Storage (From the date of receipt)
Store at 4°C for 2 years. Don’t freeze in the absence of glycerol.
Protocol
This procedure (Figure 1) offers a general guideline for immunoprecipitation (IP). Optimization may be required for each antibody and target antigen. Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP are ideally suited for IP reactions.
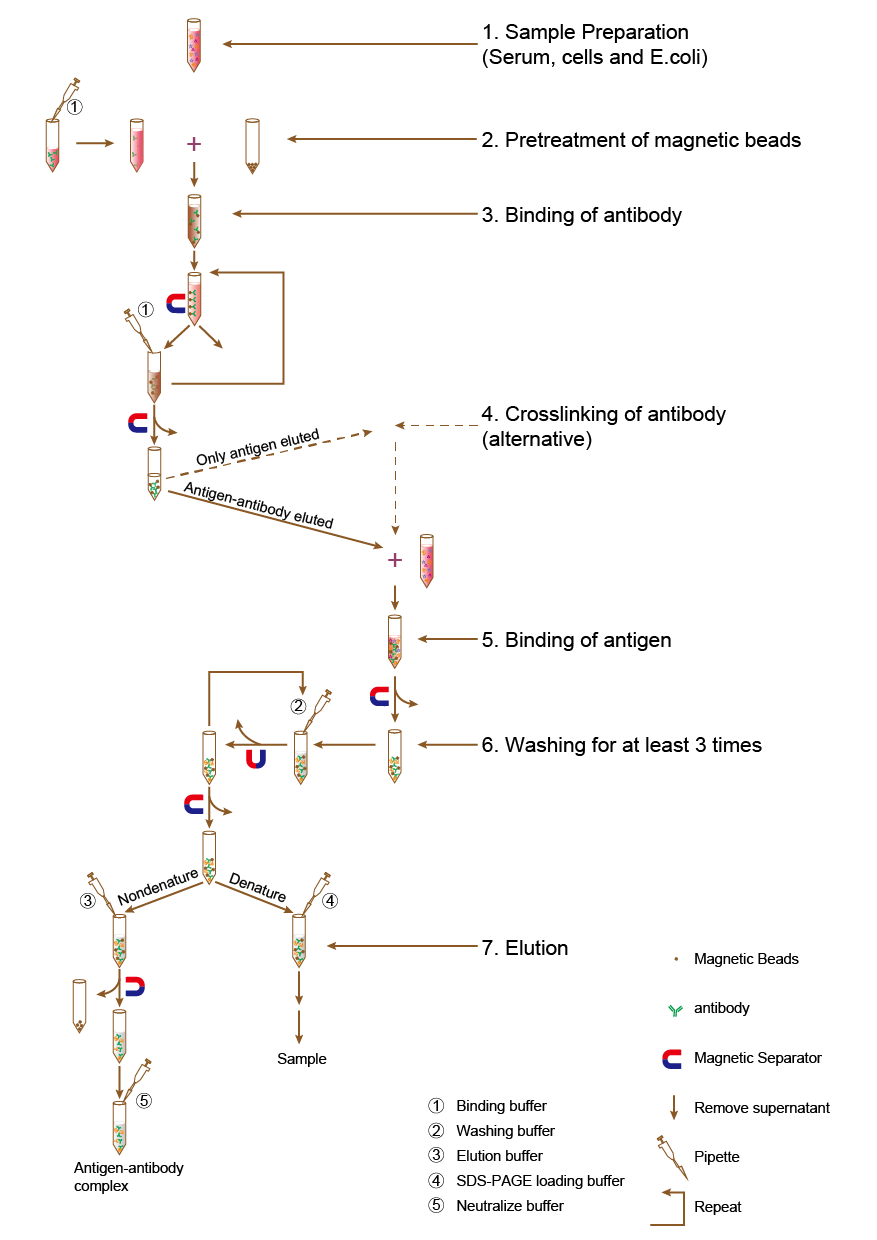
Figure 1 General Protocol for Immunoprecipitation
Recommended buffer examples
| Buffer | Contents (Prepared by customers) |
|---|---|
| Binding buffer | 50 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, 0.1%-0.5% detergent (TritonX-100, Tween 20 or NP40), pH 7.5 |
| Wash buffer | 50 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, 0.1%-0.5% detergent, pH 7.5 |
| Elution buffer | 0.1 M -0.2 M Glycine, 0.1%-0.5% detergent, pH 2.5-3.1 (or 0.1 M citric acid, 0.1%-0.5% detergent, pH 2.5-3.1) |
| Neutralize buffer | 1M Tris, pH8.0 |
Important Notes before Beginning
1. Before immunoprecipitation, please be sure to carefully read the operating instructions.
2. This product requires use of a magnetic separator.
3. Protein A/G Magnetic Beads should be suspended uniformly before use.
4. Protein A/G Magnetic Beads should be kept in storage solution and prevent dry.
5. Do not freeze or centrifuge MagBeads protein A/G.
6. In order to ensure the best results, please select an antibody with strong specificity.
7. For the IP experiments, different antibodies and antigens will display different binding affinities. Antibody and antigen binding may be altered based on use of binding buffer and washing buffer. Some operator optimization may be necessary.
8. This product is only intended to be used as directed. All other uses are prohibited.
| Species | Antibody class | sProtein A/G | sProtein A |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human | Total IgG | +++++ | +++++ |
| IgG1, IgG2 | +++++ | +++++ | |
| IgG3 | +++++ | + | |
| IgG4 | +++++ | +++++ | |
| IgM | + | + | |
| IgD | - | - | |
| IgA | + | + | |
| IgA1, IgA2 | + | + | |
| IgE | +++ | +++ | |
| Fab | + | + | |
| ScFv | + | + | |
| Mouse | Total IgG | +++++ | +++++ |
| IgM | - | - | |
| IgG1 | +++ | + | |
| IgG2a | +++ | +++ | |
| IgG2b | +++ | +++ | |
| IgG3 | +++ | +++++ | |
| Rat | Total IgG | +++ | + |
| IgG 1 | +++ | +++ | |
| IgG2a | +++++ | +++ | |
| IgG2b | + | +++ | |
| IgG2c | +++++ | +++ | |
| Cow | Total IgG | +++++ | + |
| IgG1 | +++++ | + | |
| IgG2 | +++++ | +++++ | |
| Goat | Total IgG | +++++ | + |
| IgG1 | +++++ | + | |
| IgG2 | +++++ | +++++ | |
| Sheep | Total IgG | +++++ | + |
| IgG1 | +++++ | + | |
| IgG2 | +++++ | +++++ | |
| Horse | Total IgG | +++++ | + |
| IgG(ab), IgG(c) | + | - | |
| IgG(T) | +++++ | + | |
| Rabbit | Total IgG | +++++ | +++++ |
| Guinea pig | Total IgG | +++++ | +++++ |
| Hamster | Total IgG | +++ | +++ |
| Pig | Total IgG | +++++ | +++++ |
| Donkey | Total IgG | +++++ | +++ |
| Cat | Total IgG | +++++ | +++++ |
| Dog | Total IgG | +++++ | +++++ |
| Monkey | Total IgG | +++++ | +++++ |
| Chicken | Total IgG | - | - |
Notes: "+"= weak binding, "+++"=medium binding, "+++++"=strong binding, "-"=no binding
Related Other Products
Tech Support
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.





































