- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
R788 (Fostamatinib) Disodium Syk inhibitor
Cat.No.S2206
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 624.42
Jump to
Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.99%
99.99
| Related Targets | EGFR VEGFR JAK PDGFR FGFR Src HIF FLT FLT3 HER2 |
|---|---|
| Other Syk Inhibitors | R406 R406 (free base) PRT062607 (P505-15) HCl Entospletinib (GS-9973) Piceatannol BAY 61-3606 dihydrochloride PRT-060318 2HCl TAK-659 Hydrochloride RO9021 R112 |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ramos | Function assay | Inhibition of SYK in human Ramos cells, IC50 = 0.267 μM. | 23350847 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 12 mg/mL
(19.21 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
Dilution Calculator
Molecular Weight Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
%
DMSO
%
%
Tween 80
%
ddH2O
%
DMSO
+
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 624.42 | Formula | C23H24FN6O9P.2Na |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 1025687-58-4 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | Tamatinib Fosdium | Smiles | CC1(C(=O)N(C2=C(O1)C=CC(=N2)NC3=NC(=NC=C3F)NC4=CC(=C(C(=C4)OC)OC)OC)COP(=O)([O-])[O-])C.[Na+].[Na+] | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Features |
Clinically used oral formulation of R406.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Syk
(Cell-free assay) 41 nM
|
| In vitro |
R935788 is a methylene phosphate prodrug of R406, which can be rapidly converted to R406 in vivo. R406 (in vitro active form of R935788) selectively inhibits Syk-dependent signaling with EC50 values ranging from 33 nM to 171 nM, more potently than Syk-independent pathways in different cells. R406 inhibits cellular proliferation of a variety of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cell lines with EC50 values ranging from 0.8 μM to 8.1 μM. R406 treatment reduces basal phosphorylation of BLNK, Akt, glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3), forkhead box O (FOXO) and ERK not only in cells with high (TCL-002) but also in cells with low levels of phosphorylated Syk (TCL1-551). In addition, R406 completely inhibits the anti-IgM induced Bcr signal in TCL1 leukemias. Despite the higher levels of constitutively active Syk in TCL1 leukemias, R406 is not selectively cytotoxic to the leukemic cells.
|
| Kinase Assay |
In vitro fluorescence polarization kinase assays
|
|
R406 (in vitro active form of R935788) is serially diluted in DMSO and then diluted to 1% DMSO in kinase buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM MnCl2, 1 mM DTT, 0.1 mg/mL acetylated BGG). ATP and substrate in kinase buffer are added at room temperature, resulting in a final DMSO concentration on 0.2%. The kinase reactions are performed in a final volume of 20 μL containing 5 μM HS1 peptide substrate and 4 μM ATP and started by addition of 0.125 ng of Syk in kinase buffer. The reaction is allowed to proceed for 40 minutes at room temperature. The reaction is stopped by the addition of 20 μL of PTK quench mix containing EDTA/anti-phosphotyrosine antibody (1× final)/fluorescent phosphopeptide tracer (0.5× final) diluted in FP Dilution Buffer. The plate is incubated for 30 minutes in the dark at room temperature and then read on a Polarion fluorescence polarization plate reader. Data is converted to determine the amount of phosphopeptide present using a calibration curve generated by competition with the phosphopeptide competitor provided in the Tyrosine Kinase Assay Kit. For IC50 determination, R406 is tested at eleven concentrations in duplicate and curve-fitting is performed by non-linear regression analysis using Prism GraphPad Software.
|
|
| In vivo |
Given that plasma half-life of R406 in mice is less than 2 hours, R935788 is administered in 3 divided doses at 3-hour intervals to provide continuous Syk inhibition during each day of treatment, mimicking the longer plasma half-life in humans (15 hours). Despite the relatively modest cytotoxic effect in vitro, R935788 significantly inhibits the proliferation and survival of leukemic cell in vivo, which is associated with the blocking of antigen-dependent B-cell receptor (Bcr) signaling rather than inhibition of constitutive Syk activity. R935788 treatment at 80 mg/kg/day for 18-21 days potently inhibits tumor growth of TCL1-002, TCL1-551 and TCL1-870 in mice with undetectable leukemic CD5+/B220+ cells at the last day of treatment, significantly prolongs the survival of the treated mice with median survival increased from 45/46 days to 170/172 days, and completely eradicates the malignant cells in a substantial proportion of mice after a 6-month follow-up period without affecting the production of normal B lymphocytes. R935788 treatment also induces an early and transient migration of both normal and malignant B cells from spleen and lymph nodes to peripheral blood, which is subsequently followed by selective growth inhibition of the malignant B-cell population. In addition, R935788 is also effective against spontaneously developing TCL1 leukemias in Eμ-TCL1 transgenic mice.
|
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-JAK2 / JAK2 / p-SRC / SRC / p-FAK / FAK / p-SYK / SYK / p-ERK / ERK p-SYK(525-526) / t-SYK / p-SYK(323) / p-BTK / t-BTK p-MEK / MEK / p-ERK / ERK / p-AKT / AKT |

|
29340070 |
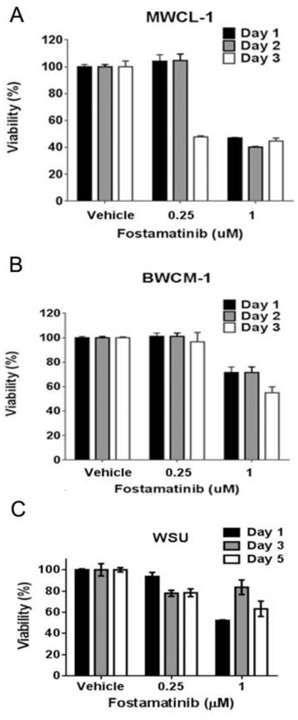
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
|
25748087 |
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05904093 | Not yet recruiting | Sickle Cell Disease|Hb-SS Disease|Hemoglobin S|Disease Sickle Cell Anemia|Sickle Cell Disorders|Hemoglobin Beta Thalassemia Disease |
National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
May 15 2024 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05509582 | Enrolling by invitation | Immune Mediated Anemia|Immune Mediated Thrombocytopenia|Chronic GVHD |
National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
May 15 2024 | Phase 2 |
| NCT06071520 | Completed | Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia |
Fundación Pública Andaluza para la gestión de la Investigación en Sevilla |
March 1 2023 | -- |
| NCT05613296 | Not yet recruiting | ITP - Immune Thrombocytopenia|Chronic ITP|Refractory ITP |
Gruppo Italiano Malattie EMatologiche dell''Adulto |
February 2023 | -- |
| NCT04543279 | Terminated | Myelofibrosis|Thrombocytopenia |
Washington University School of Medicine|Rigel Pharmaceuticals |
May 3 2021 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04904276 | Terminated | ITP|Immune Thrombocytopenia |
Rigel Pharmaceuticals |
May 18 2021 | -- |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1:
What’s the difference between S2625 and S2206?
Answer:
The differences between S2625 and S2206: 1. S2206 is more stable than S2625; 2. The water solubility of S2206 is better than S2625; 3. The absorption of S2206 is harder than S2625, so you need to test the suitable dosage if you use it in animal assays; 4. The potency of S2206 and S2625 is similar.






































