- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Sodium Dichloroacetate (DCA) PDK inhibitor
Cat.No.S8615
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 150.92
Jump to
Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.90%
99.90
| Related Targets | HSP Transferase P450 (e.g. CYP17) PDE phosphatase PPAR Vitamin Carbohydrate Metabolism Mitochondrial Metabolism Drug Metabolite |
|---|---|
| Other Dehydrogenase Inhibitors | Devimistat (CPI-613) Vorasidenib (AG-881) (R)-GNE-140 Glycyrrhizin (NSC 167409) Gossypol Acetate Emodin AGI-5198 AGI-6780 NCT-503 Brequinar |
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCF7 | Function assay | 10 mM | 12 hrs | Inhibition of PDK1 in human MCF7 cells assessed as increase in oxygen consumption rate at 10 mM after 12 hrs | 27006991 | |
| MCF7 | Function assay | 10 mM | 12 hrs | Inhibition of PDK1 in human MCF7 cells assessed as decrease in extracellular acidification rate at 10 mM after 12 hrs | 27006991 | |
| MCF7 | Function assay | 10 mM | 12 hrs | Inhibition of PDK1 in human MCF7 cells assessed as decrease in proton production rate at 10 mM after 12 hrs | 27006991 | |
| MCF7 | Function assay | 10 mM | 12 hrs | Inhibition of PDK1 in human MCF7 cells assessed as increase in ratio of oxygen consumption rate to extracellular acidification rate at 10 mM after 12 hrs | 27006991 | |
| MCF7 | Function assay | 10 mM | 12 hrs | Inhibition of PDK1 in human MCF7 cells assessed as decrease in lactate production at 10 mM after 12 hrs | 27006991 | |
| NCI-H1975 | Antiproliferative assay | 20 mM | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human NCI-H1975 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability at 20 mM after 72 hrs by MTT assay | 30470491 | |
| MCF7 | Function assay | 90 mins | Inhibition of PDK1 (unknown origin) expressed in human MCF7 cells using PDK tide as substrate measured after 90 mins in presence of ATP by ADP-Glo luminescent kinase assay | 31509699 | ||
| MCF7 | Antitumor assay | 30 mg/kg | two weeks | Antitumor activity against human MCF7 cells xenografted in BALB/c nude mouse assessed as tumor growth inhibition at 30 mg/kg, iv administered every two days for two weeks measured after 14 days | 31509699 | |
| MCF7 | Function assay | 30 uM | 4 hrs | Induction of metabolic reversal from aerobic glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation in human MCF7 cells assessed as increase in extracellular acidification rate at 30 uM pretreated for 4 hrs followed by glucose addition after 25 mins by seahorse XF24 ext | 31509699 | |
| MCF7 | Function assay | 30 uM | 4 hrs | Induction of metabolic reversal from aerobic glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation in human MCF7 cells assessed as increase in extracellular acidification rate at 30 uM pretreated for 4 hrs followed by glucose addition after 25 mins followed by subsequent assay | 31509699 | |
| MCF7 | Function assay | 30 uM | 4 hrs | Induction of metabolic reversal from aerobic glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation in human MCF7 cells assessed as decline in extracellular acidification rate at 30 uM pretreated for 4 hrs followed by glucose addition after 25 mins followed by subsequent assay | 31509699 | |
| MCF7 | Function assay | 30 uM | 6 hrs | Induction of metabolic reversal from aerobic glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation in human MCF7 cells assessed as decrease in oxygen consumption rate at 30 uM pretreated for 6 hrs followed by oligomycin A addition after 25 mins followed by subsequent assay | 31509699 | |
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
|
Molarity Calculator
Dilution Calculator
Molecular Weight Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
%
DMSO
%
%
Tween 80
%
ddH2O
%
DMSO
+
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 150.92 | Formula | C2HCl2O2.Na |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 2156-56-1 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | Dichloroacetic acid, bichloroacetic acid, BCA | Smiles | C(C(=O)[O-])(Cl)Cl.[Na+] | ||
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
PDK4
(Cell-free assay) 80 μM
PDK2
(Cell-free assay) 183 μM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Sodium Dichloroacetate (DCA) can trigger apoptosis of human lung, breast and brain cancer cells. After treatment with this compound, cancer cells show increased levels of ROS, depolarization of the MMP in vitro and increased apoptosis both in vitro and in vivo. It inhibits the activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDK), thereby stimulating the mitochondrial enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH). When turned off, PDH no longer converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA required for mitochondrial respiration and glucose dependent oxidative phosphorylation. DCA thus shifts cellular metabolism from glycolysis to glucose oxidation, decreasing the mitochondrial membrane potential gradient and helping to open mitochondrial transition pores. This metabolic switch facilitates translocation of pro-apoptotic mediators like cytochrome c (cyt c) and apoptosis inducing factor (AIF), both of which stimulate apoptosis. Thereby, it drives cancer cells to commit suicide by apoptosis.
|
| In vivo |
Sodium Dichloroacetate (DCA) can act as a cytostatic agent in vitro and in vivo, without causing apoptosis (programmed cell death). It is discovered to be a safe drug with no cardiac, pulmonary, renal or bone marrow toxicity. The most serious common side effect consists of peripheral neuropathy, which is reversible. This compound has anti-cancer activity in several cancer types including colon, prostate, ovarian, neuroblastoma, lung carcinoid, cervical, endometrial, cholangiocarcinoma, sarcoma and T-cell lymphoma. Other antineoplastic actions have also been suggested. These include angiogenesis blockade, changes in expression of HIF1-α, alteration of pH regulators V-ATPase and MCT1, and other cell survival regulators such as PUMA, GLUT1, Bcl2 and p53. It is able to significantly reduce metastatic burden in the lungs of rats in a highly metastatic in vivo model of breast cancer. In vivo the DCA-Na treatment induces 20% survival and decreased the tumoral diameter, volume and weight, without affect the body weight and avoid metastasis in C57BL/6 mice.
|
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | pPDH E1α / PDH E1α |
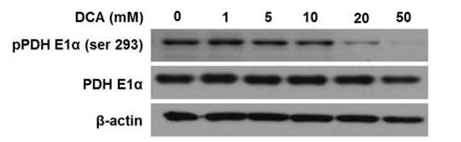
|
25630799 |
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT06073106 | Not yet recruiting | Stroke|Traumatic Brain Injury|Knee Osteoarthritis|Breast Cancer |
Tan Tock Seng Hospital|Rehabilitation Research Institute of Singapore (RRIS)|Woodlands Health (WH) |
December 2023 | -- |
| NCT05810623 | Not yet recruiting | Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Carcinoma|Bladder Cancer |
David D''Andrea|Medical University of Vienna |
June 1 2023 | Phase 3 |
| NCT05646485 | Recruiting | Bladder Cancer|Urothelial Carcinoma|Hematuria|Smoking Cessation |
University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center |
May 5 2023 | Not Applicable |
| NCT05460533 | Recruiting | B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia |
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center|Novartis Pharmaceuticals |
July 12 2022 | Phase 2 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.






































