|
Toll Free: (877) 796-6397 -- USA and Canada only -- |
Fax: +1-832-582-8590 Orders: +1-832-582-8158 |
Tech Support: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3 Please provide your Order Number in the email. |
Technical Data
| Formula | C17H16N6O3S2 |
||||||
| Molecular Weight | 416.48 | CAS No. | 2061980-01-4 | ||||
| Solubility (25°C)* | In vitro | DMSO | 83 mg/mL (199.28 mM) | ||||
| Ethanol | 2 mg/mL (4.8 mM) | ||||||
| Water | Insoluble | ||||||
| In vivo (Add solvents to the product individually and in order) |
|
||||||
|
* <1 mg/ml means slightly soluble or insoluble. * Please note that Selleck tests the solubility of all compounds in-house, and the actual solubility may differ slightly from published values. This is normal and is due to slight batch-to-batch variations. * Room temperature shipping (Stability testing shows this product can be shipped without any cooling measures.) |
|||||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Biological Activity
| Description | XMU-MP-1 is an inhibitor of MST1/2 with IC50 values of 71.1±12.9 nM and 38.1±6.9 nM against MST1 and MST2, respectively. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
||||
| In vitro | XMU-MP-1 blocks MST1/2 kinase activities, thereby activating the downstream effector Yes-associated protein and promoting cell growth. XMU-MP-1 inhibits phosphorylation of MOB1 in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, with increasing ATP concentration, XMU-MP-1 exhibits a proportional increase in IC50 against MST1/2, as well as an attenuated inhibition of the MST2-mediated phosphorylation of MOB1. At concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 10 μM, XMU-MP-1 reduces the phosphorylation of endogenous MOB1, LATS1/2, and YAP in human liver carcinoma (HepG2) cells in a dose-dependent manner. Similarly, XMU-MP-1 treatment inhibits hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-stimulated MOB1 phosphorylation and MST1/2 autophosphorylation in a variety of cell lines, including mouse macrophage-like cells (RAW264.7), human osteosarcoma (U2OS), human colorectal adenocarcinoma (SW480), immortalized human retinal pigment epithelial cells (RPE1), human pleomorphic hepatocellular carcinoma (SNU-423), and HepG2, as well as primary mouse hepatocytes, without affecting the phosphorylation of JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinase), which is a positive control for H2O2 stimulation. XMU-MP-1 treatment increases YAP nuclear translocation[1]. | ||||
| In vivo | XMU-MP-1 displays excellent in vivo pharmacokinetics and is able to augment mouse intestinal repair, as well as liver repair and regeneration, in both acute and chronic liver injury mouse models at a dose of 1 to 3 mg/kg via intraperitoneal injection. XMU-MP-1 exhibits favorable pharmacokinetics in rats with a half-life of 1.2 hours and a bioavailability of 39.5%. The maximal phosphorylation inhibition of MOB1 and YAP is achieved between 1.5 and 6 hours after intraperitoneal dosing with XMU-MP-1 (1 mg/kg). XMU-MP-1 protects mice from DSS-induced colitis and ameliorates chronic liver injury[1]. |
Protocol (from reference)
| Cell Assay:[1] |
|
|---|---|
| Animal Study:[1] |
|
Customer Product Validation
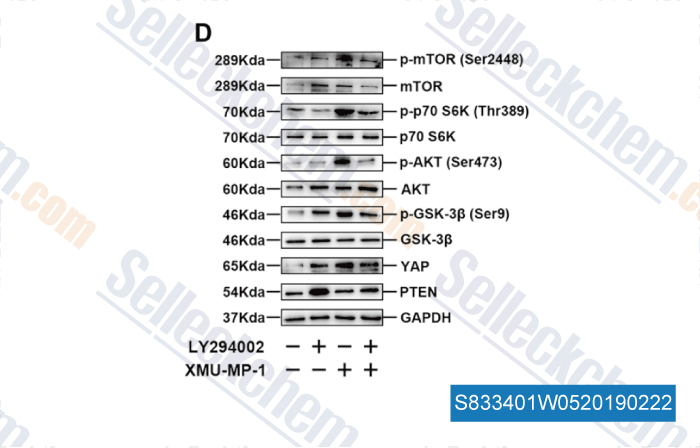
-
Data from [Data independently produced by , , FASEB J, 2019, 33(2):2514-2525]
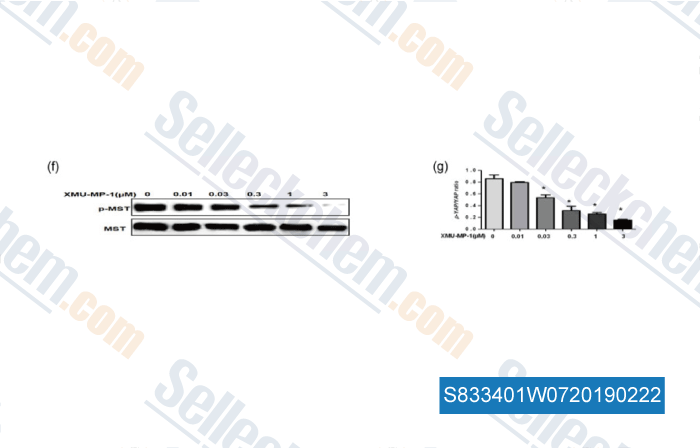
-
Data from [Data independently produced by , , J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(4):5117-5133]
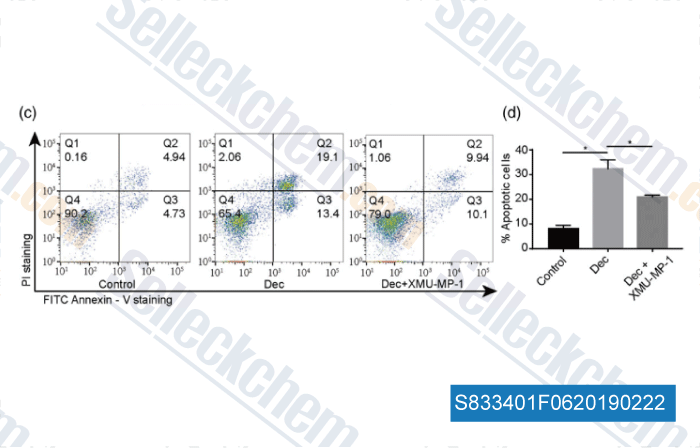
-
Data from [Data independently produced by , , Phytother Res, 2018, 32(12):2456-2465]
Selleck's XMU-MP-1 has been cited by 51 publications
| Phenylpropanoids of Eleutherococcus senticosus (Rupr. & maxim.) maxim. Alleviate oxidative stress in Alzheimer's disease in vitro and in vivo models by regulating Mst1 and affecting the Nrf2/Sirt3 pathway [ Bioorg Chem, 2025, 159:108347] | PubMed: 40081261 |
| Targeting metastasis-initiating cancer stem cells in gastric cancer with leukaemia inhibitory factor [ Cell Death Discov, 2024, 10(1):120] | PubMed: 38453889 |
| Wnt2bb signaling promotes pharyngeal chondrogenic precursor proliferation and chondrocyte maturation by activating Yap expression in zebrafish [ J Genet Genomics, 2024, S1673-8527(24)00307-2] | PubMed: 39566725 |
| SLMAP3 is crucial for organogenesis through mechanisms involving primary cilia formation [ Open Biol, 2024, 14(10):rsob240206] | PubMed: 39417621 |
| ACADL-YAP axis activity in non-small cell lung cancer carcinogenicity [ Cancer Cell Int, 2024, 24(1):86] | PubMed: 38402174 |
| CircPOLA2 sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to ferroptosis and suppresses tumorigenesis via the Merlin-YAP signaling pathway [ iScience, 2024, 27(9):110832] | PubMed: 39310771 |
| GPR137 inactivates Hippo signaling to promote gastric cancer cell malignancy [ Biol Direct, 2024, 19(1):3] | PubMed: 38163861 |
| Colonic crypt stem cell functions are controlled by tight junction protein claudin-7 through Notch/Hippo signaling [ Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2024, 10.1111/nyas.15137] | PubMed: 38598500 |
| WNT5a Signaling through ROR2 Activates the Hippo Pathway to Suppress YAP1 Activity and Tumor Growth [ Cancer Res, 2023, 83(7):1016-1030] | PubMed: 36622276 |
| Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Delay Diabetic Wound Healing by Inducing Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via the Hippo pathway [ Int J Biol Sci, 2023, 19(1):347-361] | PubMed: 36594092 |
RETURN POLICY
Selleck Chemical’s Unconditional Return Policy ensures a smooth online shopping experience for our customers. If you are in any way unsatisfied with your purchase, you may return any item(s) within 7 days of receiving it. In the event of product quality issues, either protocol related or product related problems, you may return any item(s) within 365 days from the original purchase date. Please follow the instructions below when returning products.
SHIPPING AND STORAGE
Selleck products are transported at room temperature. If you receive the product at room temperature, please rest assured, the Selleck Quality Inspection Department has conducted experiments to verify that the normal temperature placement of one month will not affect the biological activity of powder products. After collecting, please store the product according to the requirements described in the datasheet. Most Selleck products are stable under the recommended conditions.
NOT FOR HUMAN, VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE.
