|
Toll Free: (877) 796-6397 -- USA and Canada only -- |
Fax: +1-832-582-8590 Orders: +1-832-582-8158 |
Tech Support: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3 Please provide your Order Number in the email. |
Technical Data
| Formula | C21H22ClN3O3 |
||||||
| Molecular Weight | 399.87 | CAS No. | 186392-40-5 | ||||
| Solubility (25°C)* | In vitro | DMSO | 80 mg/mL (200.06 mM) | ||||
| Water | Insoluble | ||||||
| Ethanol | Insoluble | ||||||
| In vivo (Add solvents to the product individually and in order) |
|
||||||
|
* <1 mg/ml means slightly soluble or insoluble. * Please note that Selleck tests the solubility of all compounds in-house, and the actual solubility may differ slightly from published values. This is normal and is due to slight batch-to-batch variations. * Room temperature shipping (Stability testing shows this product can be shipped without any cooling measures.) |
|||||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Biological Activity
| Description | CP-91149 is a selective glycogen phosphorylase (GP) inhibitor with IC50 of 0.13 μM in the presence of glucose, 5- to 10-fold less potent in the absence of glucose. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
||
| In vitro | CP-91149 displays 200-fold higher inhibitory activity against human liver glycogen phosphorylase a (HLGPa) than caffeine (IC50 = 26 μM). CP-91149 (10-100 μM) inhibits -stimulated glycogenolysis in isolated rat hepatocytes in a dose-dependent manner, and in primary human hepatocytes with IC50 of ~2.1 μM. [1] CP-91149 also potently inhibits the activities of human muscle phosphorylase a and b with IC50 of 0.2 μM and ~0.3 μM, respectively. CP-91149 treatment at 2.5 μM induces inactivation of phosphorylase and sequential activation of glycogen synthase in hepatocytes, and increases glycogen synthesis by 7-fold at 5 mM glucose and by 2-fold at 20 mM glucose. CP-91149 can partially counteract the effects of phosphorylase overexpression. [2] CP-91149 also potently inhibits brain GP with IC50 of 0.5 μM in A549 cells. CP-91149 treatment at 10-30 μM causes significant glycogen accumulation in A549 and HSF55 cells. CP-91149 treatment increases G1-phase cells with a significant reduction of the S-phase population in HSF55 cells, correlated with increased expression of p21 and p27. [3] CP-91149 also promotes the dephosphorylation and activation of GS (glycogen synthase) in non-engineered or GP-overexpressing cultured human muscle cells, but exclusively in glucose-deprived cells. [4] |
||
| In vivo | Oral administration of CP-91149 to diabetic ob/ob mice at 25-50 mg/kg causes rapid (3 hours) glucose lowering by 100-120 mg/dl without producing hypoglycemia, resulting from inhibition of glycogenolysis in vivo. CP-91149 treatment does not lower glucose levels in normoglycemic, nondiabetic mice. [1] In the non-fasted Goto-Kakizaki (GK) rats, administration of CP-91149 in combination with CS-917 suppresses hepatic glycogen reduction by CS-917 and decreases plasma glucose more than single administration of CS-917. [5] |
Protocol (from reference)
| Kinase Assay: |
|
|---|---|
| Cell Assay: |
|
| Animal Study: |
|
References
Customer Product Validation
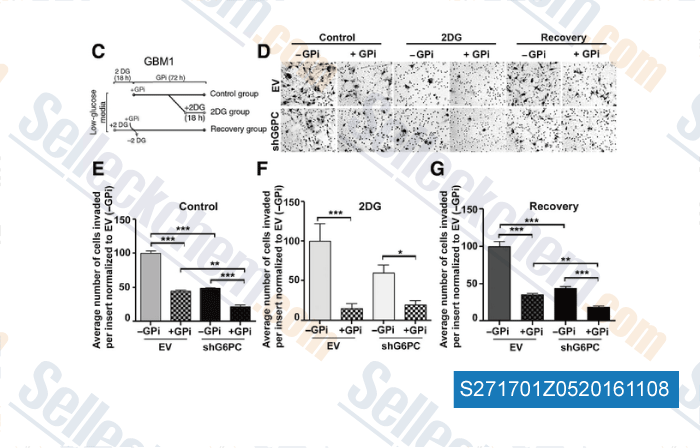
-
, , Mol Cancer Res, 2014, 12(11):1547-59.
Selleck's CP-91149 has been cited by 12 publications
| Regulation of stress granule formation in human oligodendrocytes [ Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1):1524] | PubMed: 38374028 |
| Glycogenesis and glyconeogenesis from glutamine, lactate and glycerol support human macrophage functions [ EMBO Rep, 2024, 10.1038/s44319-024-00278-4] | PubMed: 39424955 |
| Mutant IDH regulates glycogen metabolism from early cartilage development to malignant chondrosarcoma formation [ Cell Rep, 2023, 42(6):112578] | PubMed: 37267108 |
| Intracellular energy controls dynamics of stress-induced ribonucleoprotein granules [ Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1):5584] | PubMed: 36151083 |
| Intracellular energy controls dynamics of stress-induced ribonucleoprotein granules [ Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1):5584] | PubMed: 36151083 |
| TCR activation directly stimulates PYGB-dependent glycogenolysis to fuel the early recall response in CD8+ memory T cells [ Mol Cell, 2022, S1097-2765(22)00538-X] | PubMed: 35738262 |
| A genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screen identifies CENPJ as a host regulator of altered microtubule organization during Plasmodium liver infection [ Cell Chem Biol, 2022, S2451-9456(22)00205-7] | PubMed: 35738280 |
| Analysis of the expression, function and signaling of glycogen phosphorylase isoforms in hepatocellular carcinoma [ Oncol Lett, 2022, 24(2):244] | PubMed: 35761940 |
| Glycogen Metabolism Supports Early Glycolytic Reprogramming and Activation in Dendritic Cells in Response to Both TLR and Syk-Dependent CLR Agonists. [ Cells, 2020, 9(3)] | PubMed: 32183271 |
| Glycogen Metabolism Supports Early Glycolytic Reprogramming and Activation in Dendritic Cells in Response to Both TLR and Syk-Dependent CLR Agonists [ Cells, 2020, 9(3)E715] | PubMed: 32183271 |
RETURN POLICY
Selleck Chemical’s Unconditional Return Policy ensures a smooth online shopping experience for our customers. If you are in any way unsatisfied with your purchase, you may return any item(s) within 7 days of receiving it. In the event of product quality issues, either protocol related or product related problems, you may return any item(s) within 365 days from the original purchase date. Please follow the instructions below when returning products.
SHIPPING AND STORAGE
Selleck products are transported at room temperature. If you receive the product at room temperature, please rest assured, the Selleck Quality Inspection Department has conducted experiments to verify that the normal temperature placement of one month will not affect the biological activity of powder products. After collecting, please store the product according to the requirements described in the datasheet. Most Selleck products are stable under the recommended conditions.
NOT FOR HUMAN, VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE.
