|
Toll Free: (877) 796-6397 -- USA and Canada only -- |
Fax: +1-832-582-8590 Orders: +1-832-582-8158 |
Tech Support: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3 Please provide your Order Number in the email. |
Technical Data
| Formula | C22H24BrFN4O2 |
|||
| Molecular Weight | 475.35 | CAS No. | 443913-73-3 | |
| Solubility (25°C)* | In vitro | DMSO | 4 mg/mL (8.41 mM) | |
| Water | Insoluble | |||
| Ethanol | Insoluble | |||
|
* <1 mg/ml means slightly soluble or insoluble. * Please note that Selleck tests the solubility of all compounds in-house, and the actual solubility may differ slightly from published values. This is normal and is due to slight batch-to-batch variations. * Room temperature shipping (Stability testing shows this product can be shipped without any cooling measures.) |
||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Biological Activity
| Description | Vandetanib is a potent inhibitor of VEGFR2 with IC50 of 40 nM in a cell-free assay. It also inhibits VEGFR3 and EGFR with IC50 of 110 nM and 500 nM, respectively. Not sensitive to PDGFRβ, Flt1, Tie-2 and FGFR1 with IC50 of 1.1-3.6 μM. No activity against MEK, CDK2, c-Kit, erbB2, FAK, PDK1, Akt and IGF-1R with IC50 above 10 μM. Vandetanib (ZD6474) increases apoptosis and induces autophagy by increasing the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS). | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
||||||
| In vitro | Vandetanib also inhibits VEGFR3 and EGFR with IC50 of 110 nM and 500 nM, respectively. Vandetanib is not sensitive to PDGFRβ, Flt1, Tie-2 and FGFR1 with IC50 of 1.1-3.6 μM, while almost has no activity against MEK, CDK2, c-Kit, erbB2, FAK, PDK1, Akt and IGF-1R with IC50 above 10 μM. Vandetanib inhibits VEGF-, EGF- and bFGF-stimulated HUVEC proliferation with IC50 of 60 nM, 170 nM and 800 nM, with no effect on basal endothelial cell growth. Vandetanib inhibits tumor cell growth with IC50 of 2.7 μM (A549) to 13.5 μM (Calu-6). [1] Vandetanib displays an inhibitory effect on the basal ABCG2-ATPase. Parental and ABCG2-expressing A431 cells showed similar sensitivities toward Vandetanib. Exposure to EGFR inhibitors decreases pEGFR levels in A431 cells, with Vandetanib displaying only a moderate effect. Vandetanib displays a slight but measurable effect, whereas gefitinib, pelitinib and neratinib completely inhibit ABCG2-mediated efflux of mitoxantrone from A431/ABCG2 cells, similarly to the specific ABCG2 inhibitor Ko143. [2] Vandetanib inhibits both PC3wt and PC3R cell lines with similar IC50 of 13.3 μM and 11.5 μM, respectively. [3] Vandetanib suppresses phosphorylation of VEGFR2 in HUVEC and EGFR in hepatoma cells and inhibits cell proliferation. [4] Vandetanib causes an accumulation of cells in the G0-G1 phases in GEO and OVCAR-3 cells and increases apoptosis in OVCAR-3, ZR-75-1, MCF-10A ras, and GEO cells. Vandetanib causes a dose-dependent inhibition of EGFR phosphorylation in mouse NIH-EGFR fibroblasts and human MCF-10A ras breast cancer cells, two cell lines that overexpress the human EGFR. Vandetanib treatment results in a dose-dependent inhibition of soft agar growth in seven human cell lines (breast, colon, gastric, and ovarian) with functional EGFR but lacking VEGFR2. [5] | ||||||
| In vivo | Vandetanib (2.5 mg/kg, i.v.), reverses a VEGF-induced hypotension by 63% but does not significantly affect a bFGF-induced hypotension. Vandetanib (100 mg/kg) inhibits the tumor-induced blood vessel formation by 79%. Vandetanib (12.5-100 mg/kg, orally) shows great tumor growth inhibition in human tumor xenografts including Calu-6, PC-3, MDA-MA-231, SKOV-3, SW620, A549, A431, B16-F10(AP3) and Lewis Lung, with little effects on body weight. [1] In PC3wt xenografts, administration of Vandetanib alone exerts paradoxical tumor growth stimulating effects. In PC3R xenografts, the low dose of Vandetanib (25 mg/kg) has no significant effect relative to control, whereas the high dose (50 mg/kg) significantly inhibits tumor growth compared with control. In contrast, the high-dose combination reveals a significant negative interaction between Vandetanib 50 mg/kg and docetaxel 30 mg/kg in PC3R cells. [3] In tumor-bearing mice, Vandetanib suppresses phosphorylation of VEGFR2 and EGFR in tumor tissues, significantly decreases tumor vessel density, enhances tumor cell apoptosis, suppresses tumor growth, improves survival, reduces number of intrahepatic metastases, and up-regulates VEGF, TGF-alpha and EGF in tumor tissues. Treatment with Vandetanib is not associated with serious adverse events, including ALT abnormality, bone marrow suppression or body weight loss. [4] Vandetanib treatment of nude mice bearing palpable GEO colon cancer xenografts (which are sensitive to inhibition of EGFR signaling) induces dose-dependent tumor growth inhibition. [5] |
Protocol (from reference)
| Kinase Assay: |
|
|---|---|
| Cell Assay: |
|
| Animal Study: |
|
References
Customer Product Validation
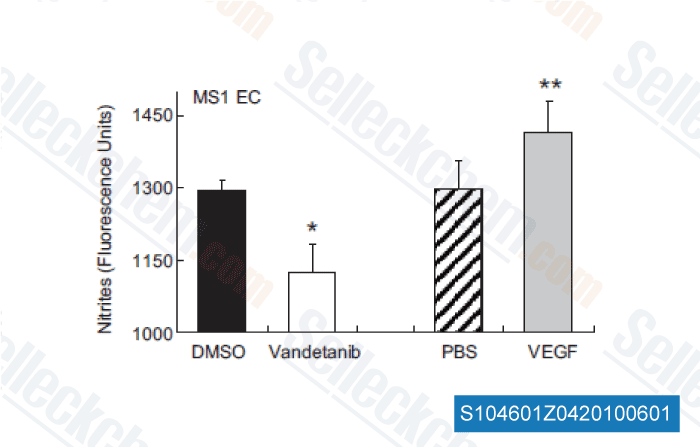
-
Data from [Hypertension, 2011, 58, 85-92]
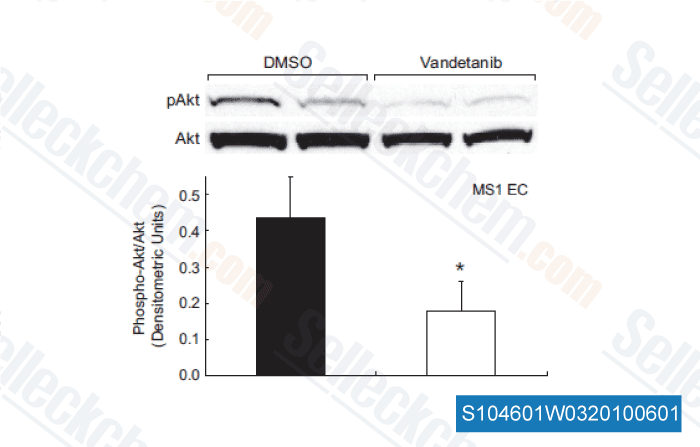
-
Data from [Hypertension, 2011, 58, 85-92]
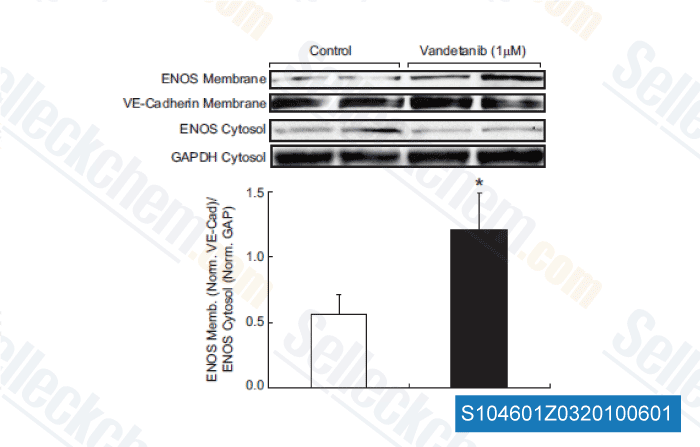
-
Data from [Hypertension, 2011, 58, 85-92]
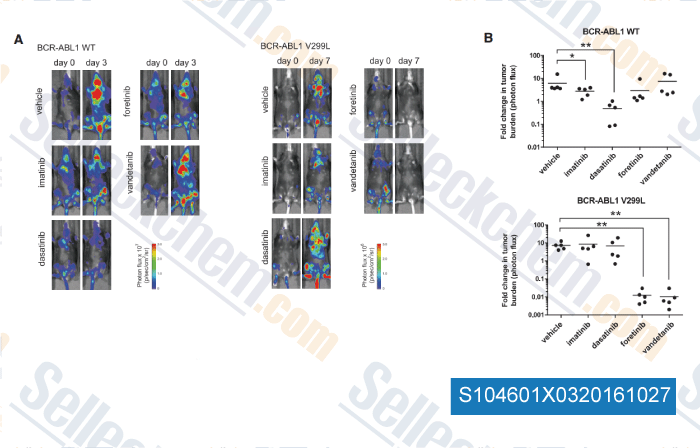
-
, , Cell, 2016, 165(1):234-46.
Selleck's Vandetanib has been cited by 119 publications
| Novel therapeutic strategies targeting bypass pathways and mitochondrial dysfunction to combat resistance to RET inhibitors in NSCLC [ Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2024, 1870(6):167249] | PubMed: 38768929 |
| Vandetanib as a prospective anti-inflammatory and anti-contractile agent in asthma [ Front Pharmacol, 2024, 15:1345070] | PubMed: 38799165 |
| Vandetanib as a prospective anti-inflammatory and anti-contractile agent in asthma [ Front Pharmacol, 2024, 15:1345070] | PubMed: 38799165 |
| Vepafestinib is a pharmacologically advanced RET-selective inhibitor with high CNS penetration and inhibitory activity against RET solvent front mutations [ Nat Cancer, 2023, 4(9):1345-1361] | PubMed: 37743366 |
| ETV2 primes hematoendothelial gene enhancers prior to hematoendothelial fate commitment [ Cell Rep, 2023, 42(6):112665] | PubMed: 37330911 |
| Nuclear translocation of cGAS orchestrates VEGF-A-mediated angiogenesis [ Cell Reports, 2023, 112328] | PubMed: None |
| Nuclear translocation of cGAS orchestrates VEGF-A-mediated angiogenesis [ Cell Rep, 2023, 42(4):112328] | PubMed: 37027305 |
| Phosphate-induced activation of VEGFR2 leads to caspase-9-mediated apoptosis of hypertrophic chondrocytes [ iScience, 2023, 26(9):107548] | PubMed: 37636062 |
| Phosphate-induced activation of VEGFR2 leads to caspase-9-mediated apoptosis of hypertrophic chondrocytes [ iScience, 2023, 26(9):107548] | PubMed: 37636062 |
| Phosphate-induced activation of VEGFR2 leads to caspase-9-mediated apoptosis of hypertrophic chondrocytes [ iScience, 2023, 26(9):107548] | PubMed: 37636062 |
RETURN POLICY
Selleck Chemical’s Unconditional Return Policy ensures a smooth online shopping experience for our customers. If you are in any way unsatisfied with your purchase, you may return any item(s) within 7 days of receiving it. In the event of product quality issues, either protocol related or product related problems, you may return any item(s) within 365 days from the original purchase date. Please follow the instructions below when returning products.
SHIPPING AND STORAGE
Selleck products are transported at room temperature. If you receive the product at room temperature, please rest assured, the Selleck Quality Inspection Department has conducted experiments to verify that the normal temperature placement of one month will not affect the biological activity of powder products. After collecting, please store the product according to the requirements described in the datasheet. Most Selleck products are stable under the recommended conditions.
NOT FOR HUMAN, VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE.
