|
Toll Free: (877) 796-6397 -- USA and Canada only -- |
Fax: +1-832-582-8590 Orders: +1-832-582-8158 |
Tech Support: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3 Please provide your Order Number in the email. |
Technical Data
| Formula | C21H22Cl2FN5O |
|||
| Molecular Weight | 450.34 | CAS No. | 877399-52-5 | |
| Solubility (25°C)* | In vitro | DMSO | 45 mg/mL (99.92 mM) | |
| Water | Insoluble | |||
| Ethanol | Insoluble | |||
|
* <1 mg/ml means slightly soluble or insoluble. * Please note that Selleck tests the solubility of all compounds in-house, and the actual solubility may differ slightly from published values. This is normal and is due to slight batch-to-batch variations. * Room temperature shipping (Stability testing shows this product can be shipped without any cooling measures.) |
||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Biological Activity
| Description | Crizotinib is a potent inhibitor of c-Met and ALK with IC50 of 11 nM and 24 nM in cell-based assays, respectively. It is also a potent ROS1 inhibitor with Ki value less than 0.025 nM. Crizotinib induces autophagy through inhibition of the STAT3 pathway in multiple lung cancer cell lines. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
||||||
| In vitro | PF-2341066 displays similar potency against c-Met phosphorylation in mIMCD3 mouse or MDCK canine epithelial cells with IC50 of 5 nM and 20 nM, respectivly. PF-2341066 shows improved or similar activity against NIH3T3 cells engineered to express c-Met ATP-binding site mutants V1092I or H1094R or the P-loop mutant M1250T with IC50 of 19 nM, 2 nM and 15 nM, respectively, compared with NIH3T3 cells expressing wild-type receptor with IC50 of 13 nM. In contrast, a marked shift in potency of PF-2341066 is observed against cells engineered to express c-Met activation loop mutants Y1230C and Y1235D with IC50 of 127 nM and 92 nM, respectively, compared with wild-type receptor. PF-2341066 also potently prevents the phosphorylation of c-Met in NCI-H69 and HOP92 cells, with IC50 of 13 nM and 16 nM, respectively, which express the endogenous c-Met variants R988C and T1010I, respectively. PF-2341066 is >1,000-fold selective for the VEGFR2 and PDGFRβ RTKs, >250-fold selective for IRK and Lck, and ∼40- to 60-fold selective for Tie2, TrkA, and TrkB, all compared with c-Met. PF-2341066 is 20- to 30-fold selective for RON and Axl RTKs. In contrast, PF-2341066 shows a near-equivalent IC50 of 24 nM against the nucleophosmin (NPM)-anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) oncogenic fusion variant of the ALK RTK expressed by the KARPAS299 human anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) cell line. PF-2341066 inhibits c-Met–dependent neoplastic phenotypes of cancer cells and angiogenic phenotypes of endothelial cells. PF-2341066 suppresses human GTL-16 gastric carcinoma cell growth with IC50 of 9.7 nM. PF-2341066 induces apoptosis in GTL-16 cells with IC50 of 8.4 nM. PF-2341066 inhibits HGF-stimulated human NCI-H441 lung carcinoma cell migration and invasion with IC50 of 11 nM and 6.1 nM, respectively. PF-2341066 inhibits MDCK cell scattering with IC50 of 16 nM. PF-2341066 prevents HGF-stimulated c-Met phosphorylation, cell survival, and Matrigel invasion with IC50 of 11 nM, 14 nM and 35 nM, respectively. In addition, PF-2341066 prevents serum-stimulated HMVEC branching tubulogenesis (formation of vascular tubes) in fibrin gels. [1] PF-2341066 also potently inhibits NPM-ALK phosphorylation in Karpas299 or SU-DHL-1 ALCL cells with an IC50 of 24 nM. PF-2341066 potently prevents cell proliferation, which is associated with G(1)-S-phase cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis in ALK-positive ALCL cells with IC50 of 30 nM, but not ALK-negative lymphoma cells. [2] Besides, PF-2341066 prevents osteosarcoma behavior associated with primary tumor growth (i.e., proliferation and survival) as well as metastasis (eg, invasion and clonogenicity). [3] |
||||||
| In vivo | In the GTL-16 model, PF-2341066 reveals the ability to cause marked regression of large established tumors (>600 mm3) in both the 50 mg/kg/day and 75 mg/kg/day treatment cohorts, with a 60% decrease in mean tumor volume over the 43-day administration schedule. In an another study, PF-2341066 displays the ability to completely inhibits GTL-16 tumor growth for >3 months, with only 1 of 12 mice exhibiting a significant increase in tumor growth over the 3-month treatment schedule at 50 mg/kg/day. In the NCI-H441 NSCLC model, a 43% decrease in mean tumor volume is observed at 50 mg/kg/day during the 38-day PF-2341066 administration cycle. In the Caki-1 RCC model, a 53% decrease in mean tumor volume is observed to be associated with decreased volume of each tumor by at least 30% at 50 mg/kg/day during the 33-day PF-2341066 administration cycle. PF-2341066 also reveals near-complete prevention of the growth of established tumors at 50 mg/kg/day in the U87MG glioblastoma or PC-3 prostate carcinoma xenograft models, with 97% or 84% inhibition on the final study day, respectively. In contrast, PF-2341066 p.o. given at 50 mg/kg/day does not significantly inhibit tumor growth in the MDA-MB-231 breast carcinoma model, or the DLD-1 colon carcinoma model. A significant dose-dependent reduction of CD31–positive endothelial cells is observed at 12.5 mg/kg/day, 25 mg/kg/day, and 50 mg/kg/day in GTL-16 tumors, indicating that inhibition of MVD shows a dose-dependent correlation to antitumor efficacy. PF-2341066 displays a significant dose-dependent reduction of human VEGFA and IL-8 plasma levels in both the GTL-16 and U87MG models. Marked inhibition of phosphorylated c-Met, Akt, Erk, PLCλ1, and STAT5 levels is observed in GTL-16 tumors following p.o. administration of PF-2341066.[1] P.o. administration of PF-2341066 to severe combined immunodeficient-Beige mice bearing Karpas299 ALCL tumor xenografts leads to dose-dependent antitumor efficacy with complete regression of all tumors at the 100 mg/kg/d dose within 15 days of initial compound administration. In addition, inhibition of key NPM-ALK signaling mediators, including phospholipase C-gamma, signal transducers and activators of transcription 3, extracellular signal-regulated kinases, and Akt by PF-2341066 are observed at concentrations or dose levels, which correlated with inhibition of NPM-ALK phosphorylation and function.[2] PF-2341066 prevents osteosarcoma behavior associated with primary tumor growth (eg, proliferation and survival) as well as metastasis (eg, invasion and clonogenicity). In nude mice treated with PF-2341066 via oral gavage, the growth and associated osteolysis and extracortical bone matrix formation of osteosarcoma xenografts are prevented by PF-2341066.[3] Treatment of c-MET-amplified GTL-16 xenografts with 50 mg/kg PF-2341066 elicits tumor regression that is associated with a slow reduction in 18F-FDG uptake and decreases expression of the glucose transporter 1, GLUT-1.[4] |
Protocol (from reference)
| Kinase Assay: |
|
|---|---|
| Cell Assay: |
|
| Animal Study: |
|
References
Customer Product Validation
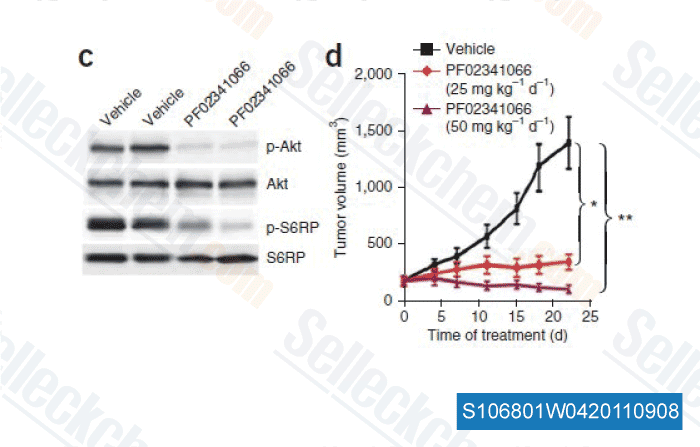
-
Data from [Nat Med, 2011, 17, 1116-1120]
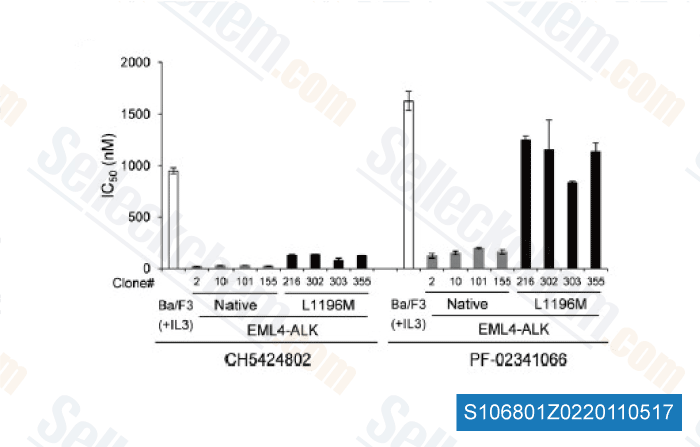
-
Data from [Cancer Cell, 2011, 19, 679–690]
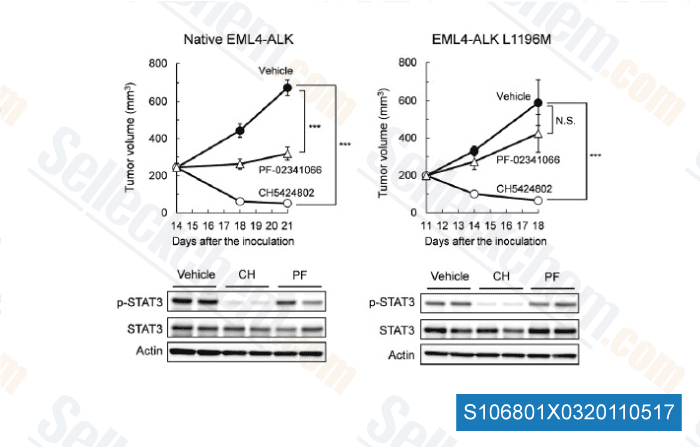
-
Data from [Cancer Cell, 2011, 19, 679–690]

-
Data from [J Biomol Screen, 2011, 16, 141-154]
Selleck's Crizotinib has been cited by 507 publications
| NVL-655 Is a Selective and Brain-Penetrant Inhibitor of Diverse ALK-Mutant Oncoproteins, Including Lorlatinib-Resistant Compound Mutations [ Cancer Discov, 2024, OF1-OF20.] | PubMed: 39269178 |
| Targeting ALK averts ribonuclease 1-induced immunosuppression and enhances antitumor immunity in hepatocellular carcinoma [ Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1):1009] | PubMed: 38307859 |
| Multi-omic and functional analysis for classification and treatment of sarcomas with FUS-TFCP2 or EWSR1-TFCP2 fusions [ Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1):51] | PubMed: 38168093 |
| The Dual Role of the NFATc2/galectin-9 Axis in Modulating Tumor-Initiating Cell Phenotypes and Immune Suppression in Lung Adenocarcinoma [ Adv Sci (Weinh), 2024, 11(20):e2306059] | PubMed: 38528665 |
| The Dual Role of the NFATc2/galectin-9 Axis in Modulating Tumor-Initiating Cell Phenotypes and Immune Suppression in Lung Adenocarcinoma [ Adv Sci (Weinh), 2024, 11(20):e2306059] | PubMed: 38528665 |
| Targeting of vulnerabilities of drug-tolerant persisters identified through functional genetics delays tumor relapse [ Cell Rep Med, 2024, 5(3):101471] | PubMed: 38508142 |
| Combined inhibition of MET and VEGF enhances therapeutic efficacy of EGFR TKIs in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer with concomitant aberrant MET activation [ Exp Hematol Oncol, 2024, 13(1):97] | PubMed: 39354638 |
| Recurrent somatic mutations of FAT family cadherins induce an aggressive phenotype and poor prognosis in anaplastic large cell lymphoma [ Br J Cancer, 2024, ] | PubMed: 39478125 |
| TWIST1 is a critical downstream target of the HGF/MET pathway and is required for MET driven acquired resistance in oncogene driven lung cancer [ Oncogene, 2024, 10.1038/s41388-024-02987-5] | PubMed: 38485737 |
| LTK mutations responsible for resistance to lorlatinib in non-small cell lung cancer harboring CLIP1-LTK fusion [ Commun Biol, 2024, 7(1):412] | PubMed: 38575808 |
RETURN POLICY
Selleck Chemical’s Unconditional Return Policy ensures a smooth online shopping experience for our customers. If you are in any way unsatisfied with your purchase, you may return any item(s) within 7 days of receiving it. In the event of product quality issues, either protocol related or product related problems, you may return any item(s) within 365 days from the original purchase date. Please follow the instructions below when returning products.
SHIPPING AND STORAGE
Selleck products are transported at room temperature. If you receive the product at room temperature, please rest assured, the Selleck Quality Inspection Department has conducted experiments to verify that the normal temperature placement of one month will not affect the biological activity of powder products. After collecting, please store the product according to the requirements described in the datasheet. Most Selleck products are stable under the recommended conditions.
NOT FOR HUMAN, VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE.
