|
Toll Free: (877) 796-6397 -- USA and Canada only -- |
Fax: +1-832-582-8590 Orders: +1-832-582-8158 |
Tech Support: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3 Please provide your Order Number in the email. |
Technical Data
| Formula | C23H23ClN2O5S |
|||
| Molecular Weight | 474.96 | CAS No. | 355025-24-0 | |
| Solubility (25°C)* | In vitro | DMSO | 94 mg/mL (197.91 mM) | |
| Ethanol | 94 mg/mL (197.91 mM) | |||
| Water | Insoluble | |||
|
* <1 mg/ml means slightly soluble or insoluble. * Please note that Selleck tests the solubility of all compounds in-house, and the actual solubility may differ slightly from published values. This is normal and is due to slight batch-to-batch variations. * Room temperature shipping (Stability testing shows this product can be shipped without any cooling measures.) |
||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Biological Activity
| Description | Ki16425 is a competitive, potent and reversible antagonist to LPA1, LPA2 and LPA3 with Ki of 0.34 μM, 6.5 μM and 0.93 μM in RH7777 cell lines, respectively, shows no activity at LPA4, LPA5, LPA6. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
||||||
| In vitro | Kil6425 preferentially inhibits LPA1- and LPA3-mediated responses but has only a moderate effect on LPA2. Ki16425 inhibits the LPA-induced Ca(2+) response in THP-1 cells, 3T3 fibroblasts, and A431 cells, but had only a marginal effect in PC-12 cells and HL-60 cells, which means that Ki16425 seems to be a useful tool for evaluating the involvement of specific LPA receptors in the short-term response to LPA. Ki16425 inhibits long-term DNA synthesis and cell migration as induced by LPA in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. [1] Ki16425 reduces the LPA-induced activation of p42/p44 mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK), while acting as a weak stimulator of p42/p44 MAPK on its own, properties typical of a protean agonist. Ki16425 also significantly reduces the NGF-induced stimulation of p42/p44 MAPK and inhibited NGF-stimulated neurite outgrowth in PC-12 cells. [2] Ki16425 markedly inhibits the expressions of COX-2 protein induced by synovial fluids. The enhancement of the IL-1 action by LPA on COX-2 expression is also inhibited by Ki16425. [3] | ||||||
| In vivo | Ki-16425 (30 mg/kg, i.p.) completely blocks LPA-induced neuropathic pain-like behaviors, when administered 30 min but not 90 min before lysophosphatidic acid injection, suggesting that Ki-16425 is a short-lived inhibitor. Ki-16425 also inhibits nerve injury-induced up-regulation of Caα2δ-1 in the dorsal root ganglion and reduction of SP immunoreactivity in the spinal dorsal horn. [4] |
Protocol (from reference)
| Animal Study:[4] |
|
|---|
References
Customer Product Validation

-
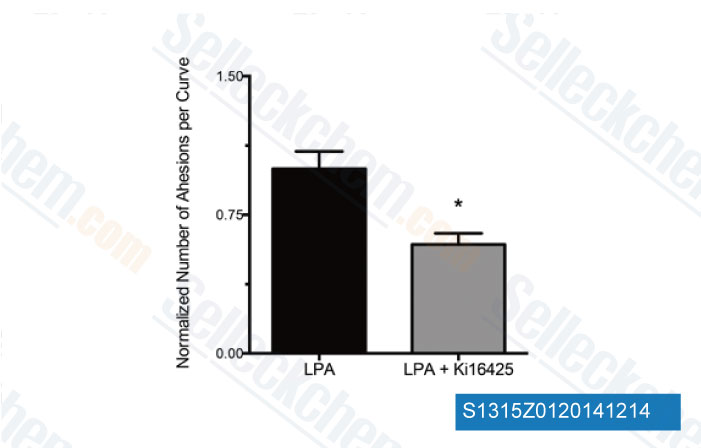
Data from [J Cell Mol Med, 2014, 18(1), 156-69]
-
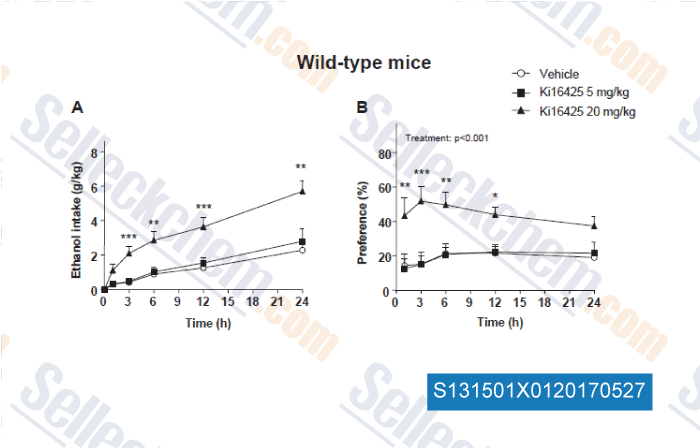
Data from [Data independently produced by Front Physiol, 2014, 5, 413]
-
Data from [Data independently produced by , , Neuropharmacology, 2016, 103:92-103]

-
Data from [Data independently produced by , , Int J Mol Med, 2016, 37(2):468-74]
Selleck's Ki16425 has been cited by 27 publications
| Cancer-associated fibroblasts maintain critical pancreatic cancer cell lipid homeostasis in the tumor microenvironment [ Cell Rep, 2024, 43(11):114972] | PubMed: 39535921 |
| YAP/TAZ mediates resistance to KRAS inhibitors through inhibiting proapoptosis and activating the SLC7A5/mTOR axis [ JCI Insight, 2024, 9(24)e178535] | PubMed: 39704172 |
| Deficiency of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 3 decreases erythropoietin production in hypoxic mouse kidneys [ Lipids Health Dis, 2024, 23(1):381] | PubMed: 39558335 |
| Lysophosphatidic acid is associated with oocyte maturation by enhancing autophagy via PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway in granulosa cells [ J Ovarian Res, 2023, 16(1):137] | PubMed: 37434211 |
| Lysophosphatidic acid is associated with oocyte maturation by enhancing autophagy via PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway in granulosa cells [ J Ovarian Res, 2023, 16(1):137] | PubMed: 37434211 |
| Recapitulating early human development with 8C-like cells [ Cell Rep, 2022, 39(12):110994] | PubMed: 35732112 |
| Lysophosphatidic acid suppresses apoptosis of high-grade serous ovarian cancer cells by inducing autophagy activity and promotes cell-cycle progression via EGFR-PI3K/Aurora-AThr288-geminin dual signaling pathways [ Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13:1046269] | PubMed: 36601056 |
| LPA signaling acts as a cell-extrinsic mechanism to initiate cilia disassembly and promote neurogenesis [ Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1):662] | PubMed: 33510165 |
| Lysophosphatidic Acid-Induced EGFR Transactivation Promotes Gastric Cancer Cell DNA Replication by Stabilizing Geminin in the S Phase [ Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12:706240] | PubMed: 34658851 |
| LPA receptor1 antagonists as anticancer agents suppress human lung tumours. [ Eur J Pharmacol, 2020, 868:172886] | PubMed: 31866407 |
RETURN POLICY
Selleck Chemical’s Unconditional Return Policy ensures a smooth online shopping experience for our customers. If you are in any way unsatisfied with your purchase, you may return any item(s) within 7 days of receiving it. In the event of product quality issues, either protocol related or product related problems, you may return any item(s) within 365 days from the original purchase date. Please follow the instructions below when returning products.
SHIPPING AND STORAGE
Selleck products are transported at room temperature. If you receive the product at room temperature, please rest assured, the Selleck Quality Inspection Department has conducted experiments to verify that the normal temperature placement of one month will not affect the biological activity of powder products. After collecting, please store the product according to the requirements described in the datasheet. Most Selleck products are stable under the recommended conditions.
NOT FOR HUMAN, VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE.
