|
Toll Free: (877) 796-6397 -- USA and Canada only -- |
Fax: +1-832-582-8590 Orders: +1-832-582-8158 |
Tech Support: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3 Please provide your Order Number in the email. |
Technical Data
| Formula | C27H29NO11.HCl |
|||
| Molecular Weight | 579.98 | CAS No. | 25316-40-9 | |
| Solubility (25°C)* | In vitro | DMSO | 100 mg/mL (172.41 mM) | |
| Water | 100 mg/mL (172.41 mM) | |||
| Ethanol | Insoluble | |||
|
* <1 mg/ml means slightly soluble or insoluble. * Please note that Selleck tests the solubility of all compounds in-house, and the actual solubility may differ slightly from published values. This is normal and is due to slight batch-to-batch variations. * Room temperature shipping (Stability testing shows this product can be shipped without any cooling measures.) |
||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Biological Activity
| Description | Doxorubicin (DOX) HCl is an antibiotic agent that inhibits human DNA topoisomerase I and topoisomerase II with IC50s of 0.8 μM and 2.67 μM, respectively. Doxorubicin reduces basal phosphorylation of AMPK. Doxorubicin is used in the concomitant treatment of HIV-infected patients but is found to be at high risk of HBV reactivation.This product may precipitate when dissolved in PBS solution. It is recommended to prepare the stock solution in pure water and dilute with either pure water or saline to obtain the working solution. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
||
| In vitro | Doxorubicin, an antibiotic anthracycline, is commonly considered to exert its anti-tumor activity at two fundamental levels, altering DNA and producing free radicals to trigger apoptosis of cancer cells through DNA damage. Doxorubicin can block the synthesis of DNA by intercalating into the DNA strand, and inhibits DNA topoisomerase II (TOP2). Doxorubicin is most effective when cells are rapidly proliferating and expressing high levels of TOP2. Additionally, Doxorubicin can trigger apoptosis by producing ceramide (which prompts apoptosis by activating p53 or other downstream pathways such as JNK), the degradation of Akt by serine threonine proteases, the mitochondrial release of cytochrome c, increased FasL (death receptor Fas/CD95 ligand) mRNA production, and a greater production of free radicals. [2] Pre-treatment with GSNO (nitrosoglutathione) suppresses the resistance in the doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer cell line MCF7/Dx, accompanied by enhanced protein glutathionylation and accumulation of doxorubicin in the nucleus. [3] Doxorubicin induced G2/M checkpoint arrest are attributed to elevated cyclin G2 (CycG2) expression and phospho-modification of proteins in the ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) and ATM and Rad3-related (ATR) signaling pathways. [5] Doxorubicin inhibits AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), resulting in SIRT1 dysfunction, p53 accumulation, and increased cell death in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and cardiomyocytes, which can be further sensitized by pre-inhibition of AMPK. [6] Doxorubicin elicits a marked heat shock response, and that either inhibition or silencing of heat shock proteins enhance the Doxorubicin apoptotic effect in neuroblastoma cells. Nanomolar Doxorubicin treatment of neuroblastoma cells causes dose-dependent over-ubiquitination of a specific set of proteins in the absence of measurable inhibition of proteasome, and loss of activity of ubiquitinated enzymes such as lactate dehydrogenase and α-enolase, the protein ubiquination patterns of which is similar to those with proteasome inhibitor, indicating that Doxorubicin may also exert its effect by damaging proteins. [8] |
||
| In vivo | In vivo, Doxorubicin in combination with adenoviral MnSOD (AdMnSOD) plus 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea (BCNU) has the greatest effect in decreasing the volumes of MB231 tumors and prolonging survival of mice. [1] Although its use is limited by the chronic and acute toxic side effects it produces, Doxorubicin is essential in treating breast and oesophageal carcinomas, solid tumours in childhood, osteosarcomas, Kaposi's sarcoma, soft tissue sarcomas, and Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas. [2] |
Protocol (from reference)
| Cell Assay: |
|
|---|---|
| Animal Study: |
|
References
Customer Product Validation
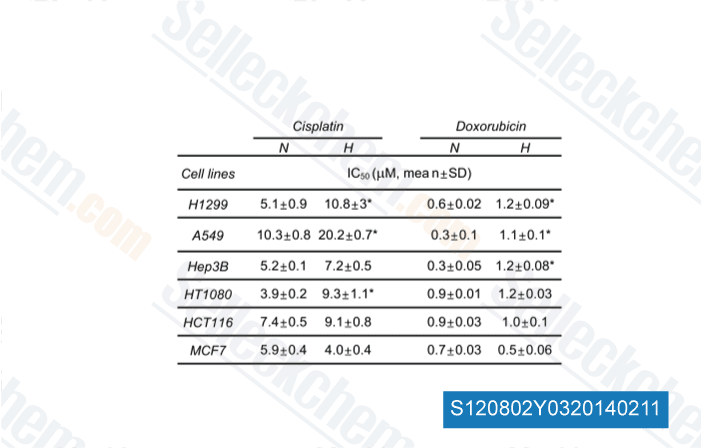
-
Data from [Cancer Res, 2014, 74, 298-308]
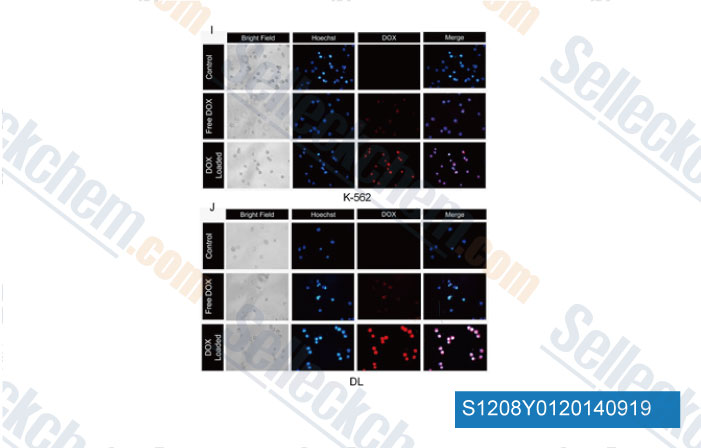
-
Data from [Data independently produced by PLoS One, 2014, 9, e94309]
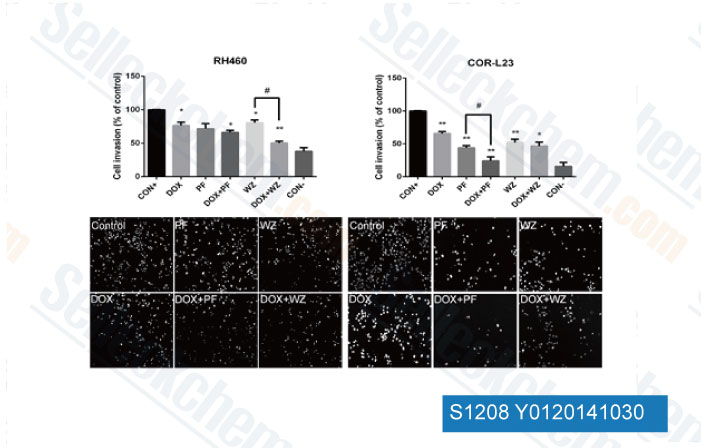
-
Data independently produced by , 2014, Dr Milica Pesic from Institute for Biological Research
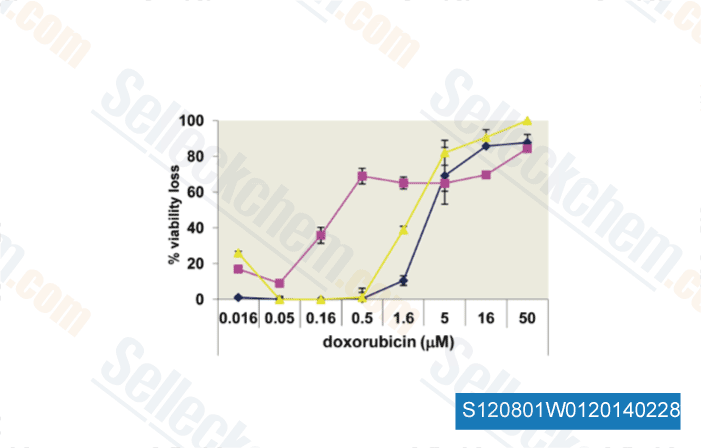
-
Data from [PLoS One, 2013, 8(1), e54595]
Selleck's Doxorubicin (DOX) HCl has been cited by 1045 publications
| Sensing steroid hormone 17α-hydroxypregnenolone by GPR56 enables protection from ferroptosis-induced liver injury [ Cell Metab, 2024, S1550-4131(24)00371-1] | PubMed: 39389061 |
| BRD-810 is a highly selective MCL1 inhibitor with optimized in vivo clearance and robust efficacy in solid and hematological tumor models [ Nat Cancer, 2024, 10.1038/s43018-024-00814-0] | PubMed: 39179926 |
| p53-dependent crosstalk between DNA replication integrity and redox metabolism mediated through a NRF2-PARP1 axis [ Nucleic Acids Res, 2024, gkae811] | PubMed: 39315696 |
| Personalized drug screening using patient-derived organoid and its clinical relevance in gastric cancer [ Cell Rep Med, 2024, 5(7):101627] | PubMed: 38964315 |
| FUNDC1 alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by restoring mitochondrial-endoplasmic reticulum contacts and blocked autophagic flux [ Theranostics, 2024, 14(9):3719-3738] | PubMed: 38948070 |
| A novel role for the ROS-ATM-Chk2 axis mediated metabolic and cell cycle reprogramming in the M1 macrophage polarization [ Redox Biol, 2024, 70:103059] | PubMed: 38316066 |
| Membrane RRM2-positive cells represent a malignant population with cancer stem cell features in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma [ J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2024, 43(1):255] | PubMed: 39243109 |
| An oncolytic vaccinia virus encoding hyaluronidase reshapes the extracellular matrix to enhance cancer chemotherapy and immunotherapy [ J Immunother Cancer, 2024, 12(3)e008431] | PubMed: 38458640 |
| Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (DLD) is a novel molecular target of bortezomib [ Cell Death Dis, 2024, 15(8):588] | PubMed: 39138149 |
| Targeting high circDNA2v levels in colorectal cancer induces cellular senescence and elicits an anti-tumor secretome [ Cell Rep, 2024, 43(4):114111] | PubMed: 38615319 |
RETURN POLICY
Selleck Chemical’s Unconditional Return Policy ensures a smooth online shopping experience for our customers. If you are in any way unsatisfied with your purchase, you may return any item(s) within 7 days of receiving it. In the event of product quality issues, either protocol related or product related problems, you may return any item(s) within 365 days from the original purchase date. Please follow the instructions below when returning products.
SHIPPING AND STORAGE
Selleck products are transported at room temperature. If you receive the product at room temperature, please rest assured, the Selleck Quality Inspection Department has conducted experiments to verify that the normal temperature placement of one month will not affect the biological activity of powder products. After collecting, please store the product according to the requirements described in the datasheet. Most Selleck products are stable under the recommended conditions.
NOT FOR HUMAN, VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC USE.
