
- Inhibitors
- By product type
- Natural Products
- Inducing Agents
- Peptides
- Antibiotics
- Antibody-drug Conjugates(ADC)
- PROTAC
- Hydrotropic Agents
- Dyes
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
By research - Antibodies
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleckchem.com to customize your library.
You could select:
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-Flag magnetic beads
- Anti-Flag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- Featured Products
- MRTX1133
- Nab-Paclitaxel
- KP-457
- IAG933
- RMC-6236 (Daraxonrasib)
- RMC-7977
- Zoldonrasib (RMC-9805)
- GsMTx4
- Navitoclax (ABT-263)
- TSA (Trichostatin A)
- Y-27632 Dihydrochloride
- SB431542
- SB202190
- MK-2206 Dihydrochloride
- LY294002
- Alisertib (MLN8237)
- XAV-939
- CHIR-99021 (Laduviglusib)
- Bafilomycin A1 (Baf-A1)
- Thiazovivin (TZV)
- CP-673451
- Verteporfin
- DAPT
- Galunisertib (LY2157299)
- MG132
- SBE-β-CD
- Tween 80
- Bavdegalutamide (ARV-110)
- Z-VAD-FMK
- Wnt-C59 (C59)
- IWR-1-endo
- (+)-JQ1
- 3-Deazaneplanocin A (DZNep) Hydrochloride
- RepSox (E-616452)
- Erastin
- Q-VD-Oph
- Puromycin Dihydrochloride
- Cycloheximide
- Telaglenastat (CB-839)
- A-83-01
- Ceralasertib (AZD6738)
- Liproxstatin-1
- Emricasan (IDN-6556)
- PMA (Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate)
- Dibutyryl cAMP (Bucladesine) sodium
- Nedisertib (M3814)
- PLX5622
- IKE (Imidazole Ketone Erastin)
- STM2457
- Saruparib (AZD5305)
- New Products
- Contact Us
research use only
Fludarabine STAT1 inhibitor
Cat.No.S1491
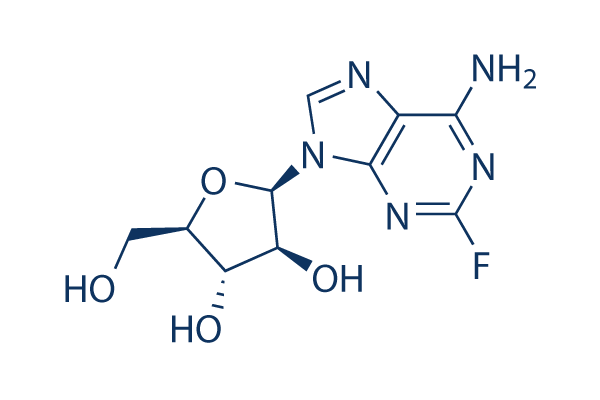
Chemical Structure
Molecular Weight: 285.23
Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.96%
99.96
Cell Culture, Treatment & Working Concentration
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jeko-1 | Function Assay | 20 μM | 24 h | inhibits expression of IDO | 25940712 | |
| MV-4-11 | Apoptosis Assay | 2.5 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 25111583 | |
| THP-1 | Apoptosis Assay | 2.5 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 25111583 | |
| MOLM 13 | Apoptosis Assay | 2.5 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 25111583 | |
| KBM3/Bu2506 | Apoptosis Assay | 2.5 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 25111583 | |
| Nalm-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18 μM | 25061101 | |||
| Reh | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30 μM | 25061101 | |||
| U2937 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16 μM | 25061101 | |||
| Mec-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50>500 μM | 25061101 | |||
| RPMI-8226 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=500 μM | 25061101 | |||
| Molt-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=180 μM | 25061101 | |||
| Nalm-6-FluR | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=250 μM | 25061101 | |||
| Raji | Function Assay | 3 μM | 24/48/72 h | induces accumulations of p53, p63 and p73 | 24940695 | |
| PBMC | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 24 h | DMSO | inhibits STAT1 phosphorylation | 24911872 |
| MDA-231 | Function Assay | 100 μM | 24 h | DMSO | decreases IDO expression | 24911872 |
| 624.38mel | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24 h | DMSO | decreases IDO expression | 24911872 |
| MDA-231 | Function Assay | 50-200 μM | 24 h | DMSO | inhibits IDO activity independently of mRNA levels | 24911872 |
| 624.38mel | Function Assay | 50-200 μM | 24 h | DMSO | inhibits IDO activity independently of mRNA levels | 24911872 |
| HMECs | Function Assay | 100 μM | 36 h | inhibits IFNγ and LPS induced STAT1 phosphorylation and IRF1 expression | 24211327 | |
| HMECs | Function Assay | 100 μM | 36 h | inhibits IFNα mediated phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT3, but not of STAT2 | 24211327 | |
| BJAB | Apoptosis Assay | 5 μM | 24 h | induces cell apoptosis | 24057147 | |
| I-83 | Apoptosis Assay | 5 μM | 24 h | induces cell apoptosis | 24057147 | |
| NALM6 | Apoptosis Assay | 5 μM | 24 h | induces cell apoptosis | 24057147 | |
| DU-145 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-10 μg/ml | 48 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose-dependent manner | 23734815 | |
| Nalm-6 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 1/2/4 h | induces autophagy | 23681223 | |
| Reh | Function Assay | 10 μM | 1/2/4 h | induces autophagy | 23681223 | |
| Nalm-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50 ∼10 μM | 23681223 | |||
| Reh | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50 ∼10 μM | 23681223 | |||
| HEC1A | Growth Inhibition Assay | 100-500 μM | 24 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose-dependent manner | 23595697 | |
| AN3CA | Growth Inhibition Assay | 100-500 μM | 24 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose-dependent manner | 23595697 | |
| HEC50B | Growth Inhibition Assay | 100-500 μM | 24 h | inhibits cell growth slightly | 23595697 | |
| HEC1A | Apoptosis Assay | 20/100 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner | 23595697 | |
| AN3CA | Apoptosis Assay | 20/100 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner | 23595697 | |
| HEC50B | Apoptosis Assay | 20/100 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 23595697 | |
| EHEB | Apoptosis Assay | 40 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis | 23497075 | |
| A549 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.7±2.8 µM | 23377192 | |||
| A549 GAPDH-deficient | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.5±2.3 µM | 23377192 | |||
| CLL | Apoptosis Assay | 10 μM | 24-96 h | induces apoptotic cell death | 22207686 | |
| MEC1 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 μM | 72 h | induces apoptosis significantly | 22132973 | |
| U937 | Apoptosis Assay | 0.8 μM | 4-48 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 22074700 | |
| U937 | Apoptosis Assay | 1 μM | 96 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 22023523 | |
| Daudi | Apoptosis Assay | 20 μM | 96 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 22023523 | |
| J45.01 | Apoptosis Assay | 1 μM | 96 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 22023523 | |
| RPMI 8226 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.9 ± 3.7 μM | 21948264 | |||
| CEM | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.4 ± 0.4 μM | 21948264 | |||
| Raji | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.47 ± 0.04 μM | 21948264 | |||
| U937 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.24 ± 0.04 μM | 21948264 | |||
| K562 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.44 ± 0.05 μM | 21948264 | |||
| NALM-6 | Apoptosis Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | induces cell apoptosis slightly | 21699383 | |
| JMV-3 | Apoptosis Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | induces cell apoptosis slightly | 21699383 | |
| EHEB | Function Assay | 5-50 μM | 24 h | decreases p21 expression significantly | 21168391 | |
| JVM-2 | Function Assay | 30 μM | 24 h | decreases p21 expression | 21168391 | |
| KBM3/Bu2506 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=0.67 µM | 20933509 | |||
| KBM3/Bu2506 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.6 μM | 24 h | increases the cell fraction in S-phase | 20933509 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.0 μM | 20447390 | |||
| MCF-7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.0 μM | 20447390 | |||
| HLE-B3 | Function Assay | 25 μM | 48 h | blocks IFN-γ–induced STAT1 phosphorylation and IDO expression | 20435158 | |
| K562 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=3.3 nM | 20307198 | ||
| BW-225 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=1.37 ×10−8 μM | 18661380 | |||
| OH-65 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=1.37 ×10−8 μM | 18661380 | |||
| GR-145 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=2.74 × 10−8 μM | 18661380 | |||
| A549 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=5.48 × 10−8 μM | 18661380 | |||
| CaSki | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=1.37 × 10−7 μM | 18661380 | |||
| ZMK-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=1.37 × 10−6 μM | 18661380 | |||
| SKW6.4 | Apoptosis Assay | 0.01-10 μM | 24/48 h | induces cell death in both time- and dose- dependent manner | 18092340 | |
| RPMI 8226 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 24 h | IC50=1.54 μM | 17976186 | ||
| MM.1S | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | IC50=13.48 μM | 17976186 | ||
| MM.1R | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | IC50=33.79 μM | 17976186 | ||
| U937 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3,200 ± 560 nM | 15930361 | |||
| CLL5 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL5 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 0.16 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| K562 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human paclitaxel-resistant K562 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 0.26 μM. | 20605656 | ||
| CLL3 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL3 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 0.35 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| CLL4 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL4 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 0.64 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| CEM-DNR-B | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human CEM-DNR-B cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 1.01 μM. | 20605656 | ||
| primary CLL | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human primary CLL cells, LD50 = 1.1 μM. | 25148392 | |||
| CLL6 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL6 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 1.6 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| CLL2 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL2 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 2.66 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| HCT116 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human HCT116 cells after 72 hrs by SRB assay, IC50 = 6.6 μM. | 25462277 | ||
| PBMC | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against patient PBMC after 48 hrs by CellTitre-Blue assay in presenc of mouse M210B4 cells, IC50 = 10 μM. | 25562417 | ||
| CHO | Function assay | Binding affinity determined by displacement of specific binding of [125I]N-(4-amino-3-iodophenethyl)-adenosine in membranes of CHO cells stably transfected with the rat adenosine A3 receptor, Ki = 10.4 μM. | 7707320 | |||
| JVM2 | Antitumor assay | Antitumor activity against human JVM2 cells assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 10.4 μM. | 24673739 | |||
| HeLa | Antitumor assay | Antitumor activity against human HeLa cells assessed as cell viability by MTT assay, EC50 = 16 μM. | 24673739 | |||
| CLL1 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL1 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 17.1 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| CEM | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human CEM cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 19.49 μM. | 20605656 | ||
| T47D | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human T47D cells after 72 hrs by SRB assay, IC50 = 46.2 μM. | 25462277 | ||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human A549 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 47.44 μM. | 20605656 | ||
| CCRF-CEM | Function assay | 10 uM | 1 to 60 mins | Drug transport in human CCRF-CEM cells assessed as ENT1-mediated uptake at 10 uM after 1 to 60 mins by liquid scintillation counting analysis | 23388705 | |
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Daoy | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for Daoy cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D caspase screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Chemical Information, Storage & Stability
| Molecular Weight | 285.23 | Formula | C10H12FN5O4 |
Storage (From the date of receipt) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS No. | 21679-14-1 | Download SDF | Storage of Stock Solutions |
|
|
| Synonyms | FaraA, Fludarabinum, NSC 118218 | Smiles | C1=NC2=C(N=C(N=C2N1C3C(C(C(O3)CO)O)O)F)N | ||
Solubility
|
In vitro |
DMSO : 57 mg/mL ( (199.83 mM) Moisture-absorbing DMSO reduces solubility. Please use fresh DMSO.) Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molarity Calculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Mechanism of Action
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
STAT1 [5]
(Vascular smooth muscle cells) |
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Fludarabine efficiently inhibits the proliferation of RPMI 8226 cells with IC50 of 1.54 μg/mL. The IC50 of this compound against MM.1S and MM.1R cells is 13.48 μg/mL and 33.79 μg/mL, respectively. In contrast, U266 cells are resistant to this chemical with IC50 of 222.2 μg/mL. This compound treatment results in increased number of cells in the G1 phase of cell cycle, accompanied with a concomitant reduction of cells at the S phase of cell cycle in a time-dependent manner. It induces a cell cycle block and triggers apoptosis in MM cells. It triggers time-dependent cleavage of caspase-8, -9, and -3, -7, followed by PARP cleavage. It increases expression of Bax in a time-dependent fashion, while the expression of Bak doesn't change. After exposure to this chemical for 12 hours, RPMI 8226 cells shows a loss of membrane potential with 61.05% of the cells expressing low fluorescence of rhodamine 123 compared with 8.62% of cells in untreated control. [1] To enhance solubility, it is formulated as the monophosphate (F-ara-AMP, fudarabine), which is instantaneously and quantitatively dephosphorylated to the parent nucleoside upon intravenous infusion. Inside the cells rephosphorylation occurs which leads to fuoroadenine arabinoside triphosphate (F-ara-ATP), the major cytotoxic metabolite of F-ara-A. [2] It can also induce pro-inflammatory stimulation of monocytic cells, as evaluated by increased expression of ICAM-1 and IL-8 release. [3] This compound does not affect the growth of ovarian cancer cell lines, whereas it induces marked and dose-dependent inhibition of proliferation in melanoma cell lines. [4] It is an inhibitor of STAT1 that specifically reduces STAT1 without affecting other STAT family members[5]. In addition to cytoplasmic accumulation, repeated low-dose cisplatin (RLDC) induces HMGB1 expression, which is marked suppressed by STAT1 knockdown. Consistently, this chemical suppresses HMGB1 expression during RLDC treatment dose-dependently in RLDC-treat renal tubular cells[5]. |
| In vivo |
Tumors treated with PBS grow rapidly to approximately 10-fold their initial volume in 25 day, whereas, the tumors in the Fludarabine at 40 mg/kg increase less than 5-fold. A significant antitumor effect of 40 mg/kg of this compound on RPMI8226 tumor growth is demonstrated. RPMI8226 tumors treated with 40 mg/kg of this chemical at day 10 increase apoptotic nuclei. This compound is effective in suppressing RPMI8226 myeloma xenografts in SCID mice. [1] |
References |
|
Applications
| Methods | Biomarkers | Images | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | procaspase-9 / procaspase-3 p-p53 / p53 STAT1 |
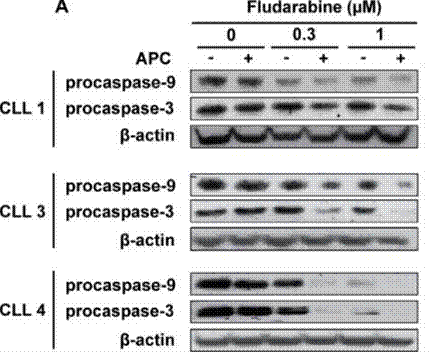
|
27223263 |
| Immunofluorescence | α-SMA / Vimentin |
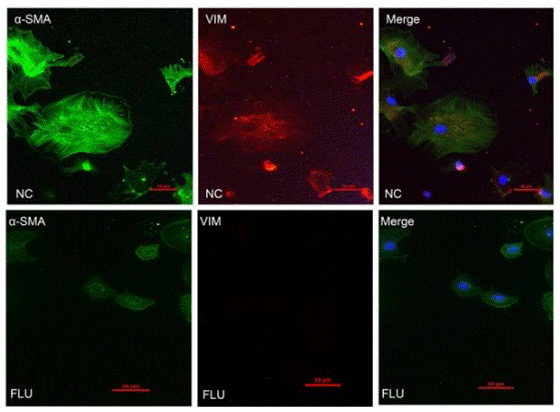
|
28322315 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
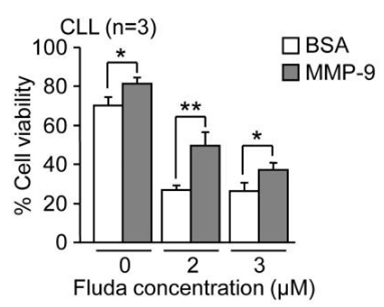
|
24956101 |
Clinical Trial Information
(data from https://clinicaltrials.gov, updated on 2024-05-22)
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05390814 | Recruiting | Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma |
Assistance Publique - Hôpitaux de Paris |
December 18 2023 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05201183 | Withdrawn | Acute Myeloid Leukemia|Chronic Myeloid Leukemia|Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia|Myelodysplastic Syndromes |
Naoyuki G. Saito M.D. Ph.D.|Indiana University |
October 2023 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT05917405 | Recruiting | Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Remission |
Nantes University Hospital |
September 14 2023 | Phase 2 |
Tech Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1:
how to re-suspend and deliver it for in vivo experiments?
Answer:
For S1491, we tested a vehicle: 30% Propylene glycol, 5% Tween 80, 65% D5W that you can resuspend this compound in at up to 30mg/ml. It is a suspension and can only be given via oral gavage.






































